Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common chronic disorder characterized by repeated episodes of upper airway obstruction during sleep. It’s defined as the cessation of breathing for at least 10-seconds. It results in low levels of oxygen in the blood and causes brief awakenings throughout the night. Symptoms may include loud snoring, disrupted sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
An overnight sleep study is required to diagnose OSA. The mainstay for treatment of OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), but there are also some natural remedies patients can try. Complications of untreated OSA may include high blood pressure, heart disease, headaches, motor vehicle accidents, depression, and even death. To better understand this condition, let’s take a look at the 7 most common causes of obstructive sleep apnea…
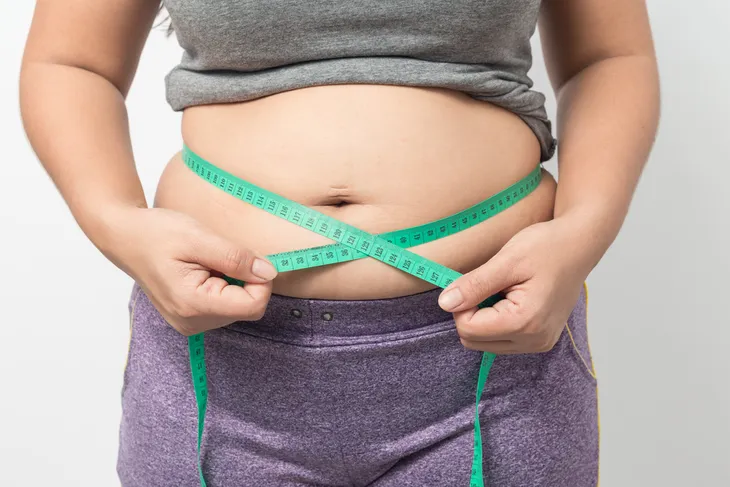
1. Excess Weight
Greater than 50-percent of individuals diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are either overweight or obese. Body mass index (BMI) is a marker used as an indirect measurement of body fat. A BMI can be calculated using mass in kilograms (kg) divided by the square of an individual’s height in meters (m). An individual BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2 is designated overweight, while a BMI of > 30 kg/m2 is designated obese.
In recent clinical studies, excess weight is the strongest risk factor associated with the development and progression of OSA in adults. Fat deposits in the tissues surrounding the upper airways cause intermittent obstruction while sleeping. A 10-percent weight gain may increase the odds of developing moderate to severe OSA by six times, while each unit increase in BMI is associated with a 14-percent increased risk of developing OSA.
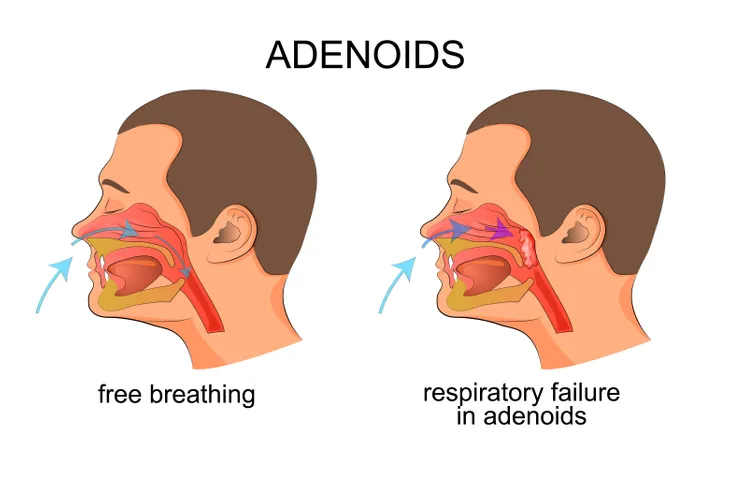
2. Enlarged Tonsils or Adenoids
Enlarged tonsils or adenoids are the most common cause of upper airway obstruction, and hence obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), in children. The tonsils represent clusters of lymphatic/immune tissue at the back of the throat, while the adenoids represent the equivalent structures at the back of the nose. Earlier clinical studies have established an association between OSA and behavior and sleep problems, low energy levels, and overall decreased daytime functioning.
A clinical study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found children undergoing surgery to remove enlarged tonsils or adenoids showed global improvement in their OSA symptoms. As a result, the surgical removal of enlarged tonsils (tonsillectomy) or adenoids (adenoidectomy) remains the primary treatment for OSA in children. Less routinely, the same surgery can be used to dramatically reduce or resolve snoring issues in adults with enlarged tonsils or adenoids.
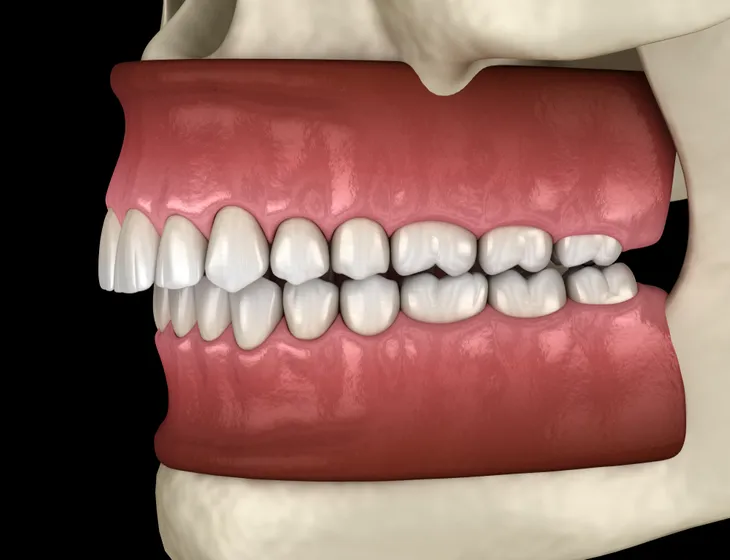
3. Excessive Overbite
An excessive overbite in which the upper teeth cover the lower teeth by more than 50-percent has the potential to cause severe snoring and may actually cause obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Mouth breathing is a common association with this degree of overbite. The lower jaw can sit quite far back with an overbite of this magnitude, which can cause narrowing of the upper airway with intermittent obstruction.
Surgery to reposition the jaw is typically the recommendation for individuals suffering from OSA induced by an excessive overbite. During the surgery (named maxillomandibular advancement), the upper and lower jaws are moved forward to increase the size of the airway. The increased size of the airway prevents upper airway obstruction and can be definitive treatment for OSA caused by an excessive overbite.
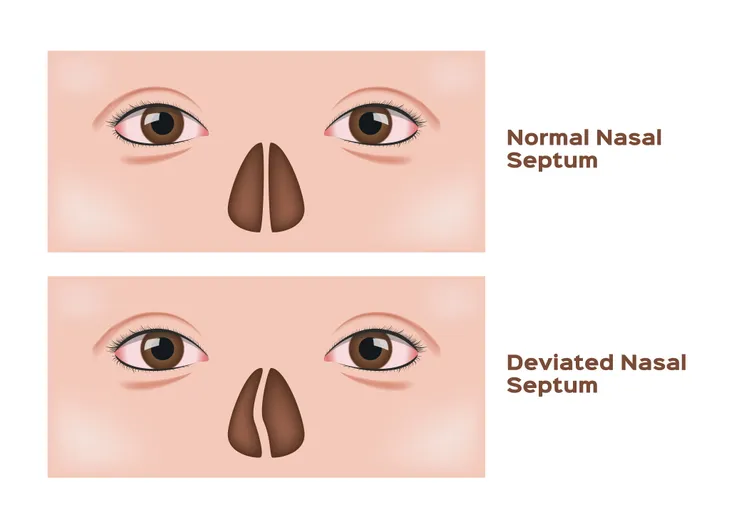
4. Deviated Nasal Septum
A deviated nasal septum may lead to the development of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It is a frequently diagnosed disorder of the nose. The septum is composed of bone and cartilage and separates the nose into right and left passages in the nasal cavity. A deviated nasal septum is most commonly caused by trauma, usually a direct blow to the face. After healing, the nasal septum leans, or deviates, right or left.
Many individuals with a deviated nasal septum experience no symptoms. Those individuals with symptoms often complain of nasal congestion, nosebleeds, snoring, or OSA. In symptomatic individuals, surgical correction of the deviated nasal septum is highly recommended. The surgery can be performed entirely through the nostrils (no external bruising or incisions) on an outpatient basis (no hospital stay). It should be noted; individuals opting for surgery typically have increased nasal congestion/obstruction post surgery that resolves over several weeks.
5. Menopause
Menopause may lead to the development of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Menopause is defined as the absence of menstrual periods in women for 12 consecutive months. During menopause, women experience ever decreasing levels of the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Both of these hormones assist in the promotion and regulation of sleep. It’s no surprise that sleep suffers as the levels of these hormones decline. In the United States, the average age of the onset of menopause is 51-years.
Researchers have demonstrated that a lack of estrogen adversely affects breathing centers in the brain, which can lead to OSA. Clinical studies have shown as estrogen levels decline rates of OSA increase. In a clinical study published in Chest, researchers discovered that 47-percent of postmenopausal women fit the criteria for the diagnosis of OSA, 21-percent of premenopausal women fit the criteria for the diagnosis of OSA, and (excluding obesity and neck circumference) rates of OSA increased due to decreasing levels of estrogen.
6. Large Neck Circumference
A large neck circumference, or the distance around the neck, may lead to the development of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). As an individual gains weight, one area of the body that increases in circumference is the neck. Additionally, fat tissue increases in other areas of the body such as the base of the tongue and tissues surrounding the upper airways. The increase in fat tissue crowds the throat and upper airways leading to intermittent obstruction.
What constitutes a large neck circumference? In clinical studies, a large neck circumference was defined as greater than 17-inches in men and greater than 15-inches in women. Neck circumference can have a significant impact on the ability to sleep. Measurement of neck circumference can be as useful as height and weight in determining the risk of OSA. The neck can easily be measured with a measuring tape (paper or plastic) in the privacy of an examination room.
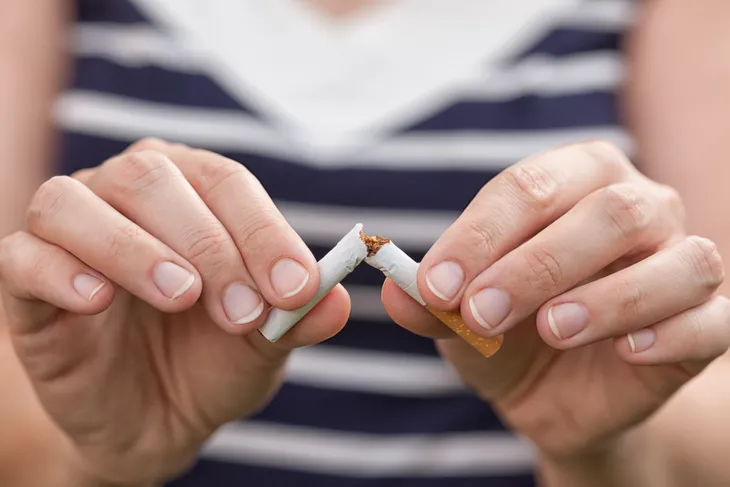
7. Smoking
Smoking may lead to the development of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Smoking irritates the tissues of the upper airways leading to inflammation. The inflammation reduces the space for air flow and can cause intermittent obstruction. In a clinical trial published in Sleeping and Breathing, researchers established smoking as an independent risk factor for the development of OSA. Current smokers are 2.5-times more likely to develop OSA.
Other mechanisms that may play a role in smoking causing OSA include poor sleep quality and increased time arousing from an episode of apnea. Smoking has been linked to sleep deprivation and sleep fragmentation (frequent awakenings), which often contributes to poor sleep quality and the development of OSA. Smoking also has been associated with a decrease in the stimulus to trigger arousal during an episode of apnea, or cessation of breathing, which can lead to longer episodes of apnea and greater levels of oxygen deprivation.