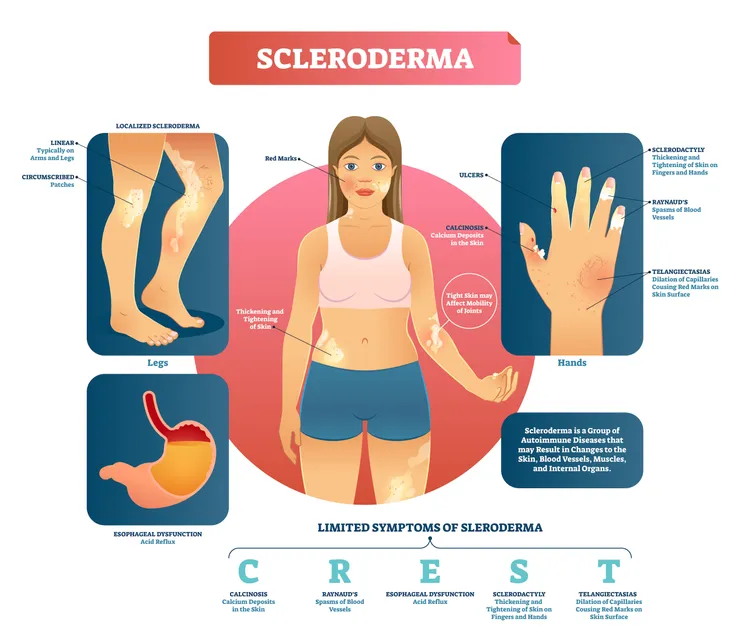
Scleroderma is a chronic disease that affects the skin, connective tissues and can even cause damage to organs. The Cleveland Clinic notes scleroderma is also known as systemic sclerosis (SSc), and affects only about 20-people per 1-million adults in the U.S. making it a rare disorder.
While there’s no cure yet, there are a number of treatment approaches to help manage the autoimmune disease. With that being said, here’s a closer look at six ways to manage it…
Medications
This is of course one of the front-line solutions to manage many conditions, although the Mayo Clinic notes, “No drug has been developed that can stop the underlying process of scleroderma — the overproduction of collagen”.
Despite this, the clinic says there are drugs that can help control the symptoms and help prevent related complications. These drugs can dilate blood vessels, suppress the immune system (autoimmune diseases are when your body attacks healthy cells), reduce stomach acid, prevent infections, and relieve pain. Consult a physician about medications that may help.
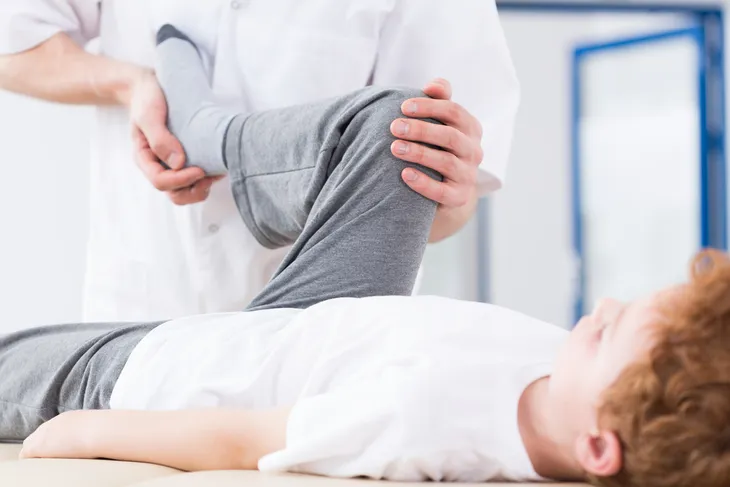
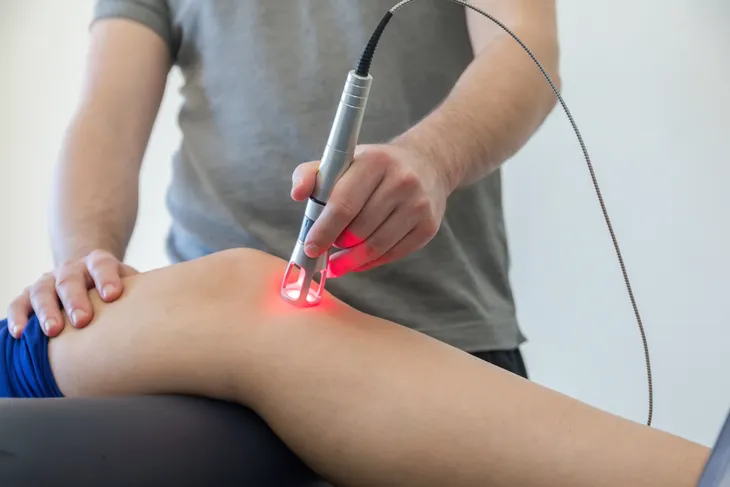
Physical Therapy
Physio-pedia.com notes physical therapy “can be very beneficial in the treatment of scleroderma,” and that stretching and gentle exercises can provide relief of some of the symptoms associated with the disease.
The source notes a program involving physical therapy can manage pain, improve strength, improve mobility, improve circulation, prevent joints from seizing, and also help achieve a better sense of overall relaxation and well being. Exercise can also help boost mood, which is a problem for many who face chronic conditions.
Surgery
This approach seems to focus on patients whose hands have been affected most by the disease. Stanford Health Care outlines a case that notes the patient ultimately had to give up the things she loves (like playing sports) due to formation of ulcers on her fingers.
When medications failed, and the pain progressed, amputation was an option that her team started to look at. However, a surgery called a digital sympathectomy was successfully used to help release scar tissue that constricts arteries, allowing proper blood flow to return to the fingers. The procedure must be performed by an experienced microvascular surgeon, adds the source.
Immunosuppressive Therapy
“The most popular approach to controlling the inflammatory phase of scleroderma is the use of immunosuppressive therapy,” explains the John Hopkins Scleroderma Center. This treatment, as mentioned earlier, can involve specific drugs to calm the immune response – namely methotrexate, cyclosporine, antithymocyte globulin, mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide, adds the source.
However, aside from drug therapy, the source also mentions research into the use of “autologous bone marrow transplantation” (stem cell transplant) combined with high-dose cyclophosphamide. “Because these aggressive forms of immunosuppressive therapy have potential risks, they should be used in severe cases of scleroderma and administered as part of a research protocol,” it notes.
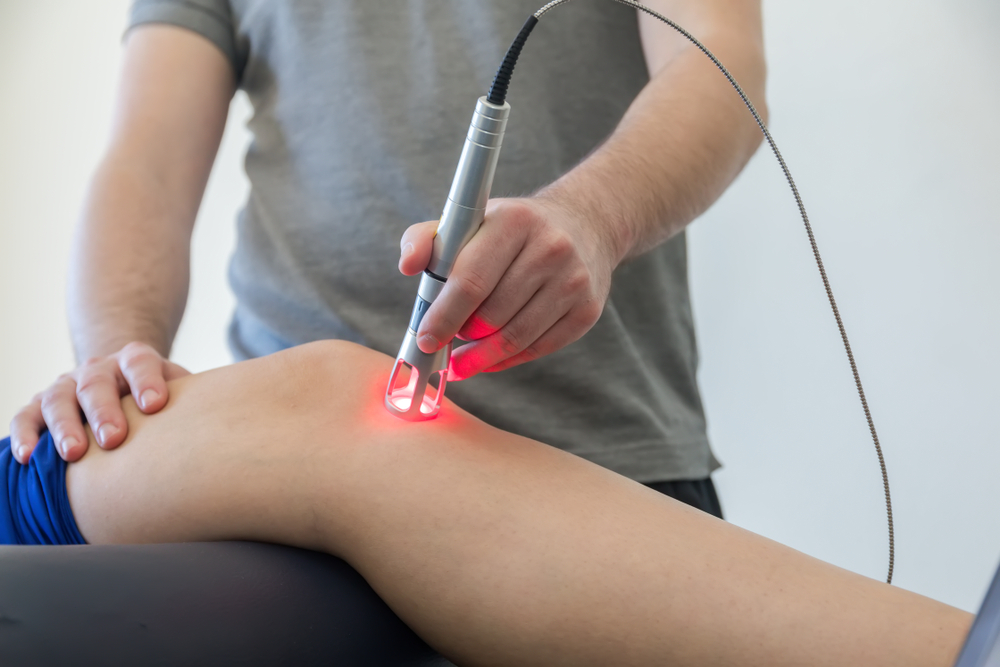
Laser Therapy
Telangiectasias – visible veins on the surface of the skin – are a problem associated with scleroderma. MedicineNet.com explains these superficial veins can show up on the face and be treated with a local laser therapy. It adds that those with the disease should avoid sun exposure, as it can make the telangiectasias worse.
Generally, precision lasers are used to heat up a vein, causing it to scar and starve it from blood flow. After the treatments, the veins theoretically will die and disappear, although it can take some time for this process to complete. UVA-1 phototherapy is another option recommended by experts as a safe way to clear up skin. These are available only in your dermatology office, and often an oral medication is given prior to light treatment for better efficacy.
Skin Lotions
Itchy and dry skin often accompanies scleroderma, which can obviously be unpleasant for the sufferer. However, there are a number of over-the-counter lotions and emollients (designed to prevent loss of skin moisture), according to HER Women’s Health and Fitness.
The site mentions a number of popular brands on skin lotions that can keep skin supple and decrease associated itchiness. It also notes brands of eye drops to manage dry eyes that can occur, as well as artificial saliva for mouth dryness caused by the disease. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you’re not sure which products will be most effective for you (prescription ointments may also be available).