Cushing’s syndrome is a serious medical condition that’s caused by exposure to high levels of cortisol in the body for long periods of time. The syndrome can occur naturally from other diseases and medical conditions that result in the production of excess cortisol, but it often occurs from taking corticosteroid medication. Cortisol is the body’s stress hormone, and it affects and controls the body’s processes in relation to metabolism and the immune system. A lot of people who have Cushing’s syndrome end up developing Cushing’s disease, as a result of the excess cortisol. Cushing’s disease is when there’s a pituitary tumor or growth that releases excess adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
Cushing’s syndrome is the result of a significant imbalance in the body and it’s important to know what to look for. Here is a look at the most common symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome…
1. Weight Gain
Rapid weight gain and obesity is one of the most common symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome, and the location of the weight gain is specific. The trunk of the body (or torso) is where the weight gain occurs, not affecting the arms or legs. Combined with the skin changes that some people with the syndrome experience, the weight gain and skinny limbs can be especially noticeable and a cause for concern.
The high levels of cortisol that the body produces causes fat to be distributed to the chest and abdominal area, as well as the face and back. When the body has too much cortisol, there aren’t enough carbohydrates for the cortisol to function the way it should by replacing fat and refueling the body. Basically, the cortisol can’t properly maintain the ideal body weight, leaving fat to build up.
2. Pink or Purple Stretch Marks
This one goes hand in hand with the weight gain as it causes stretch marks. People with Cushing’s syndrome often have pink or purplish stretch marks on their breasts, arms, abdomen, hips, and thighs. These stretch marks are sometimes referred to as “striae,” and they might be due to the fact that their skin becomes quite thin and easily bruised. The skin can also become spotted on the chest, shoulders, and face or become darkened around the neck.
3. Round Face
The face is another area of the body that is affected by Cushing’s syndrome. People with the condition often display a symptom that’s commonly referred to as a “moon face,” which is a result of the weight gain. The face is another area of the body that stores the excess fat from the increase in cortisol. The face looks round and full because of the weight gain, and it can change to a reddish color.
On top of the swelling, acne and skin infections are another sign attributable to Cushing’s syndrome. Hormonal changes are what typically cause acne in adolescents and teenagers, so it makes sense that any change, such as a spike in the body’s cortisol levels, can result in breakouts on the face. The acne could extend to the chest and neck as well. The facial weight gain and skin irritation are classic signs of the syndrome, as many will present with these symptoms.
4. High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure (hypertension) is a frequent and serious symptom of Cushing’s syndrome. How high the blood pressure is determines what symptoms are felt and the severity of the condition and having hypertension can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (a branch of the U.S. National Library of Medicine), up to 80-percent of adults with Cushing’s syndrome have high blood pressure.
The prevalence of hypertension in children and teens is lower, a little under 50-percent. The chances of high blood pressure increase greatly with ectopic Cushing’s syndrome, a form of Cushing’s syndrome that involves a tumor outside of the pituitary gland or adrenal glands. Hypertension can cause obvious symptoms and can be tested for easily, but it can also present with no symptoms when it’s not alarmingly high. If you experience symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome, you’ll likely have your blood pressure taken when you see your doctor, and it will then be monitored to reduce the risk of serious complications.
5. Muscle Weakness
Many people with Cushing’s syndrome will experience what feels like muscle weakness when they’re extremely tired; rest and relaxation can quickly cure this feeling. But unexplained fatigue and muscle weakness is a sign of Cushing’s syndrome, because the muscles begin to waste away. The excess cortisol affects how the body metabolizes nutrients—the syndrome can cause the body to be unable to process protein, a vital nutrient needed for proper functioning, development and maintenance of muscles. The loss of muscle in the limbs contributes to the arms and legs becoming noticeably skinny.
The muscle weakness is specifically targets the hips, shoulders, arms, and legs and can be so extreme that getting out of bed and other simple, everyday tasks are difficult. Cushing’s syndrome can end up causing severe muscle atrophy, which is that’s typically seen when someone is unable to move their limbs after not using them for long periods of time. A change in diet by increasing protein intake can help address this symptom.
6. Depression
There are a lot of mild to severe physical symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome that can be seen or felt, but the condition also affects the mental health of patients in addition to their physical health. Depression is often experienced by those with the syndrome, making the condition even more difficult to deal with. Glucocorticoids, medications that can cause Cushing’s syndrome, can affect emotional and mental stability, making it difficult to determine if the depression is a symptom of the syndrome or a result of the medication.
Depression is a difficult disease to deal with, and suffering from it when you have Cushing’s syndrome just adds that much more stress on your body. Since many other symptoms of the syndrome have negative physical effects, the accompanying depression can cause a sort of vicious cycle – weight gain, skin irritation, swelling, abnormal hair growth or loss, and the feelings of fatigue and muscle weakness can make people feel self-conscious. This can worsen the depression, so it’s important to address this Cushing’s symptom before it worsens.
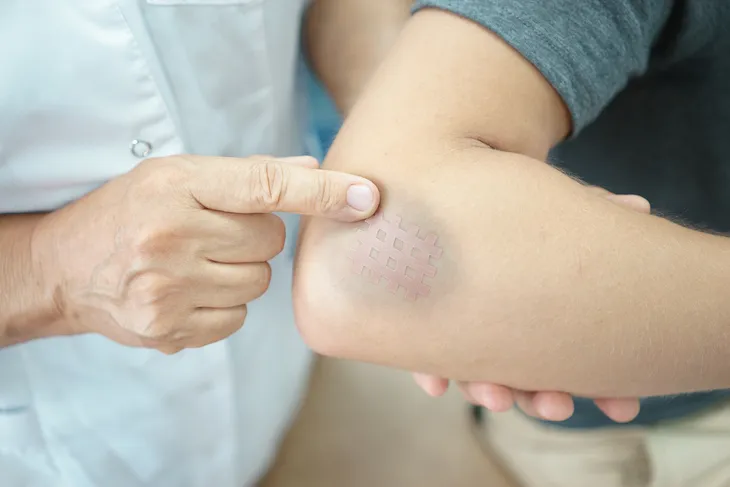
7. Bruising Easily
You probably know someone who bruises easily (or you might experience this yourself), and a lot of people just sweep this under the rug as something that isn’t worrisome. While not all causes of bruising are from serious medical conditions, one of the serious causes is Cushing’s syndrome. Lightly banging or softly running into something with a part of your body should not cause bruises, but many of those with Cushing’s syndrome will bruise from these sorts of things.
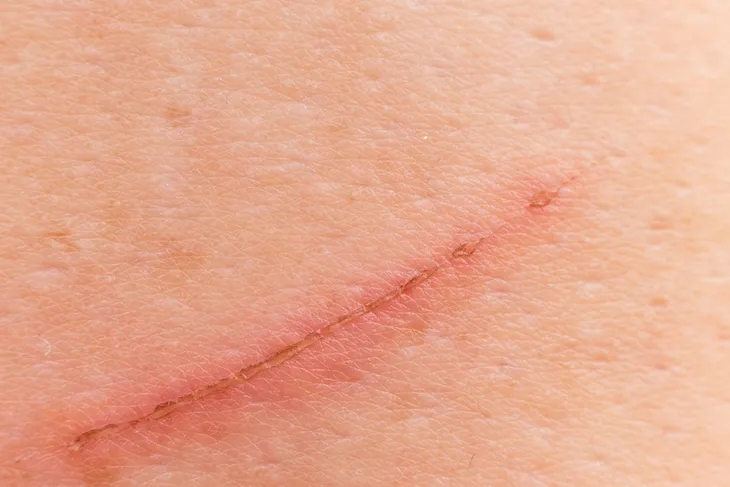
8. Slow Healing Cuts
In addition to bruising easily, slow healing wounds are another aspect of Cushing’s syndrome. The skin can become thin when you have Cushing’s syndrome, which makes wound healing difficult. The thin skin is susceptible to both bruises and cuts that form without much force, and the skin’s changes prevent the somewhat speedy healing that should occur naturally in the body. The hands are a common place where bruising and wounds occur, with excessive dryness also being present.
9. Humped Neck
Developing a hump on the back of the neck is referred to a “buffalo hump.” Cushing’s syndrome causes some of the excess fat in the body to be stored there, along with a few other specific areas of the body. The hump between the shoulder blades is one of the classic areas many people develop fatty tissue as a symptom of Cushing’s syndrome. It’s one of the most popular causes of the hump, but other causes include long-term steroid use, obesity, and osteoporosis. Any changes to your neck should be checked out by your doctor because of the potential for serious complications.
Fat deposits can also be stored on the other side of the body in the base of the neck, specifically around the collarbone and chest area. Depending on what causes Cushing’s syndrome, there are a variety of treatment options, medications, and lifestyle changes that can limit or relieve certain symptoms. Excess body fat, especially in the case of Cushing’s syndrome, can lead to obesity. Being treated to avoid further complications from being obese is crucial to the treatment of the condition.
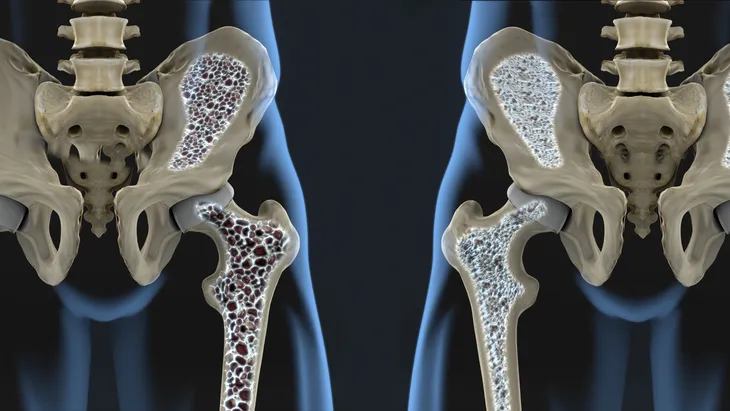
10. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition where the bones become abnormally thin, making them weak and fragile. Hormonal changes are a known cause of osteoporosis, and Cushing’s syndrome is one of them. The symptoms of osteoporosis include back pain, poor posture, and easy fractures. Osteoporosis may be known well as a disease that many elderly people develop, but it can occur from other diseases, including Cushing’s syndrome, at a much younger age. It’s a serious complication that requires treatment and monitoring.
A lot of people with Cushing’s syndrome have bone loss and end up with osteoporosis. The condition not only causes loss of bone density but also can prevent the healthy growth and formation of bone, because the body can become unable to absorb calcium, a vital nutrient for bone health. Bones can also be painful for people with Cushing’s disease. They become prone to fractures as the bone loss and osteoporosis worsens, causing significant health risks. There is treatment available that could encourage the proper development of bones, so anyone with symptoms of osteoporosis should see their doctor.
11. Menstrual Irregularities
Women who suffer from Cushing’s syndrome can experience an additional symptom that men don’t—menstrual irregularities and disturbances. The menstrual cycle can be changed, and it can even cease in some cases. Since menstrual irregularities and changes are a symptom of Cushing’s syndrome and many other medical conditions, paying attention to your cycle is necessary to ensure good health. Menstrual cycles are kind of like a woman’s built-in alarm that can identify when something in the body isn’t functioning the way it should.
When you think about it, menstrual cycles and regularity are controlled and affected by hormones, so disruptions of the hormones in a woman’s body can impact menstruation. In the case of Cushing’s syndrome, a large pituitary tumor can cause the wrong levels of hormones, ultimately affecting the menstrual cycle. This is especially true for premenopausal women and can also impact breast milk production in women that are breast-feeding.
12. Male Infertility and Erectile Dysfunction
On the flip side, just as women have gender specific symptoms, men do too. Men with Cushing’s syndrome could experience erectile dysfunction or decreased fertility. They will also likely experience decreased libido, or a low sex drive.
Medical News Today adds, “Cushing’s syndrome can affect fertility in both women and men. However, if the adrenal glands overproduce testosterone and other hormones too, this may increase libido.”
13. Abnormal Hair Changes
There are a few different ways Cushing’s syndrome affects body hair, so many types of hair growth or loss is a symptom to look for. For women, the syndrome often causes hair growth on the face in areas that men often grow hair. Women might also see abnormal hair growth on their neck and chest, and any existing facial or body hair could grow in thicker. Your hair is often a representation of your health because it’s affected by hormone levels. So, hormone imbalances can often be seen through symptoms relating to your hair.
The feel and look of hair can change for both men and women—hair can break easily because of how brittle it is and it may look and feel dry. Cushing’s syndrome can cause the opposite of hair growth, with some people suffering from hair loss and baldness. The excessively high cortisol levels are to blame. Although hair growth in areas that aren’t normal for women can occur, Cushing’s syndrome can also cause baldness and brittle hair.
14. Slow Growth Rate
Children who suffer from Cushing’s syndrome will also experience some of the other symptoms on this list such as obesity. They will feel heavy as a baby and then as they grow, it will become clear that they are developing at a slower growth rate, says WebMD.