High cholesterol is a major risk factor for some of the western world’s biggest killers, including heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, around 38 percent of adults in the United States have high cholesterol. As high cholesterol does not cause any symptoms, many of Americans don’t even realize they’re at risk.
Fortunately, cholesterol is a controllable risk factor. This means that changes to diet and lifestyle can reduce cholesterol and a person’s risk of developing serious health problems.
What Is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance produced in the liver. The human body needs at least some cholesterol to perform vital functions, like building hormones and processing high-fat foods.
Dietary cholesterol is the term used to describe additional cholesterol taken in through the foods we eat. It is predominantly found in animal products such as meat, eggs and dairy, as well as some processed foods.
Not all cholesterol is bad for your health. In fact, there are two types of cholesterol known as:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Commonly referred to as “bad” cholesterol. It can lead to fatty deposits in arteries, which increase the risk of stroke and heart disease.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Commonly referred to as “good” cholesterol. Can counteract the effects of LDL fat and reduce its associated risks.
Why Manage Cholesterol with Diet?
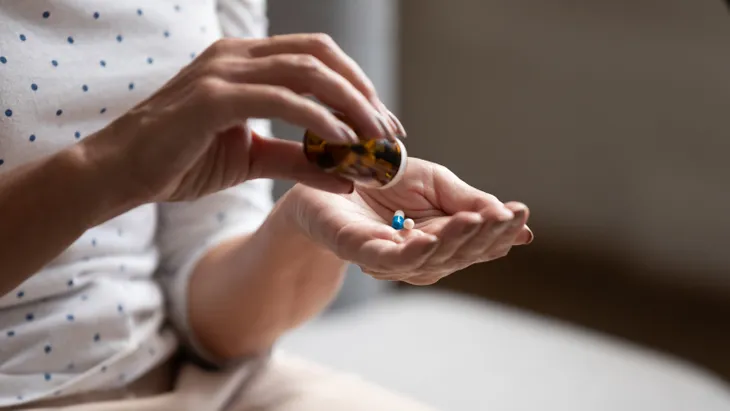
High cholesterol can also be managed with medication. The most commonly prescribed group of cholesterol-lowering drugs are known as statins.
People who have moderately high cholesterol and are committed to making lifestyle changes may be able to lower their cholesterol without medication. However, medication may be a necessity — although temporarily — for people with dangerously high cholesterol. Whether medication is necessary or not, it is important to take steps to lower your cholesterol through diet too.
Statin drugs often cause a variety of serious side-effects, including:
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Digestive issues
- Extreme fatigue
When you manage cholesterol by adopting a healthier diet, the side-effects you experience are likely to be positive.
Foods That Lower Cholesterol
Including cholesterol-lowering foods in your diet does not have to be complicated. Your focus should be on increasing your intake of high-fiber foods and foods that are rich in healthy fats. Consuming more soluble fiber can reduce cholesterol levels by binding to the fat in your gut, so it cannot enter the bloodstream so easily. Healthy fats can help by balancing out the bad cholesterol in your blood and helping to keep arteries clear and supple.
Here are four of the best foods to try:
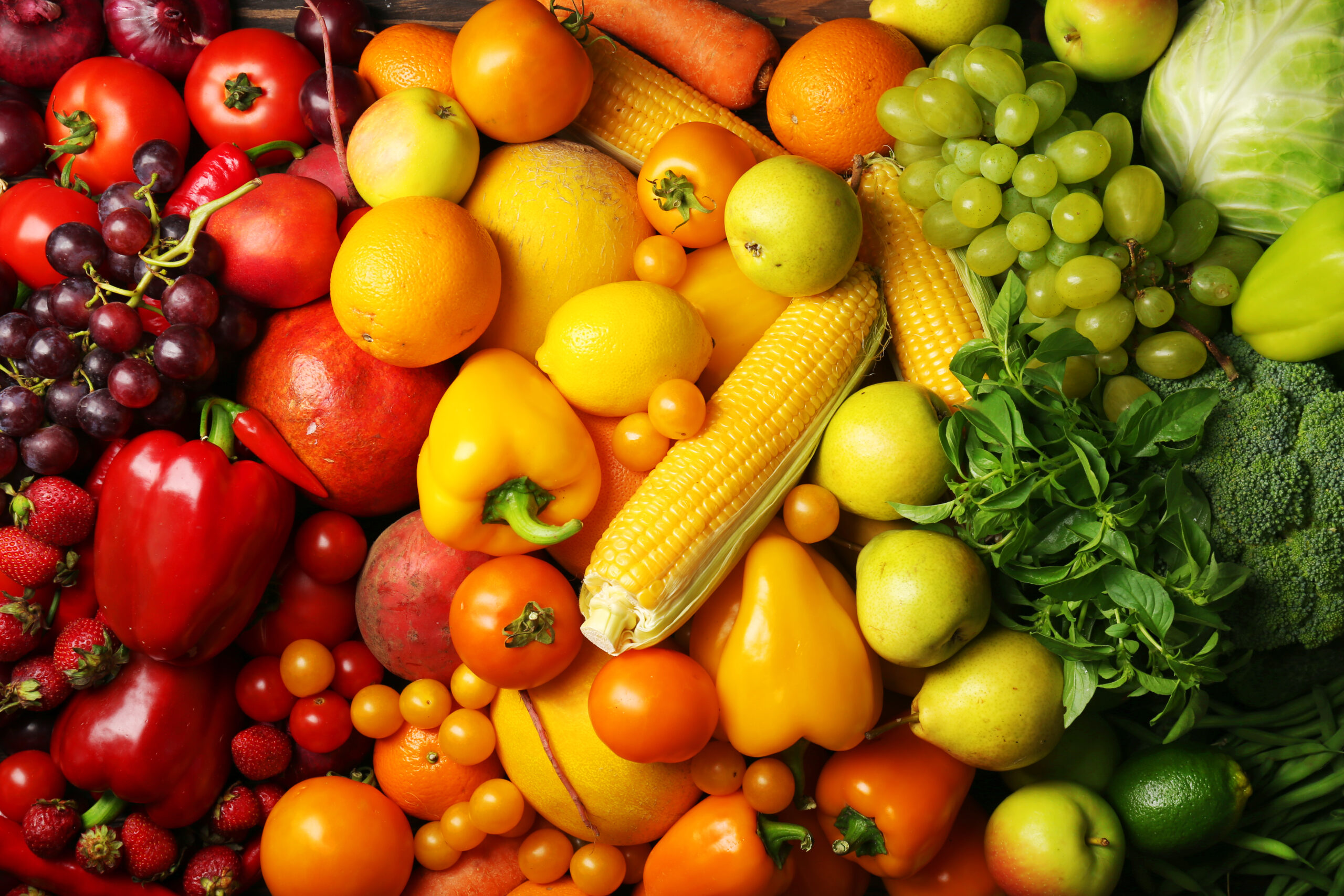
Fruits and Vegetables
Practically all fruits and vegetables are loaded with cholesterol-lowering fiber. A diet high in fruits and vegetables is an excellent weight-management tactic too, as fiber is very filling. These foods are also rich in vitamins, minerals, phytonutrients, and everything else your body needs to maintain optimum cardiovascular health.
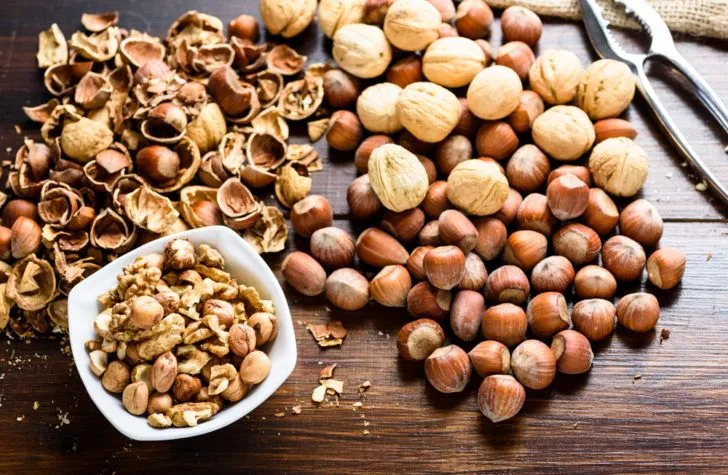
Unsaturated Fats
Consuming healthy fats is one of the smartest dietary changes you can make. Foods that are rich in unsaturated fats include:
- Nuts and seeds
- Avocado
- Olives
- Oily fish, such as sardines and mackerel
- Unprocessed vegetable oils like olive and nut oils
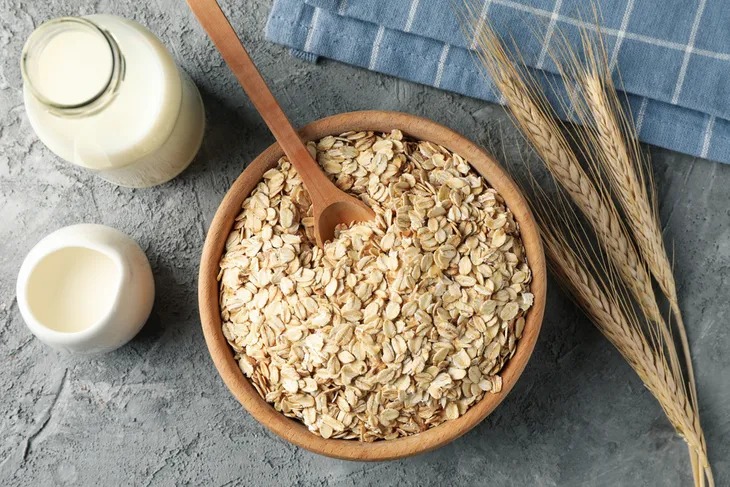
Barley and Oats
These two grains are rich in a particularly beneficial fiber known as beta glucan, which binds cholesterol in the intestines. Beta glucan also encourages the liver to make more bile, limiting cholesterol production as a result. Porridge, oatcakes, and wholegrain breakfast cereals are good sources of whole oats and barley.
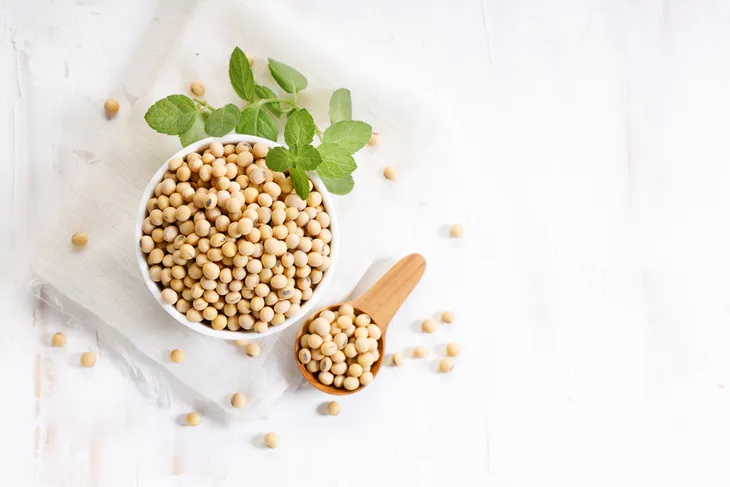
Soy-Based Foods
Switching out dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt for soy-based alternatives is a great way to reduce your dietary cholesterol intake. Soy is low in saturated fat. It is also packed with vitamins, minerals, protein, and other health-promoting nutrients.
Foods Which Increase Cholesterol
Reducing your intake of animal products is one of the most important things you can do to limit dietary cholesterol. All cholesterol comes from animal products, as it can only be produced in a liver. Trans fats can also raise cholesterol levels and should be avoided at all costs.
Here are four high-cholesterol foods to avoid:
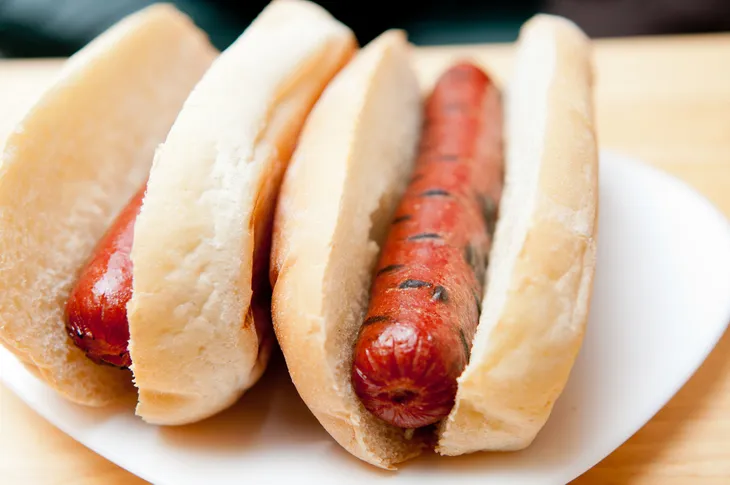
Processed Meat
Processed meats, such as sausage, bacon, and hot dogs, are extremely high in cholesterol. Additionally, studies have shown that a single 50g serving of processed meat each day can increase a person’s risk of cardiovascular disease by 42 percent. Unprocessed meat does contain cholesterol but may be included in small amounts, as part of a balanced diet.
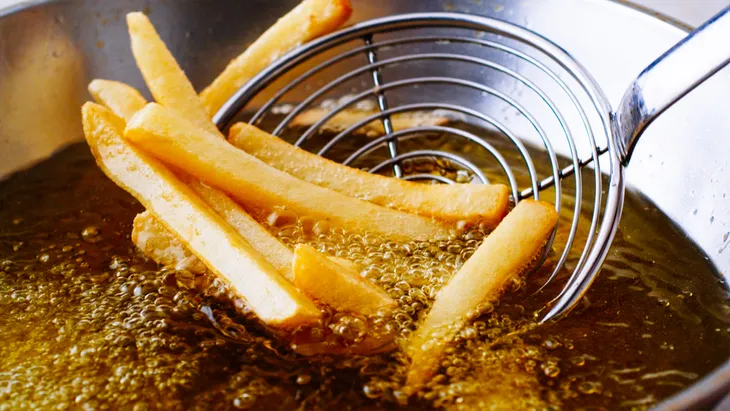
Fried Food
Fried foods are extremely high in trans fat. This type of fat is solid at room temperature and can contribute to fatty deposits in the arteries. Consuming fried foods also increases the risk of obesity-related diseases.
Dairy Products
Dairy products, such as cheese, milk, yoghurt, cream, and frozen yogurt, are all high in bad cholesterol and should be limited as much as possible. If you do choose to consume dairy, go for skim, low-fat, and fat-free options to minimize cholesterol intake.
Fast Food
Fast food has no place in a cholesterol-lowering diet. Most fast foods are extremely high in cholesterol and trans fat. Moreover, they are a huge risk factor in most chronic inflammatory diseases. Removing fast food from the diet is also beneficial as it makes way for healthier, home-cooked wholefoods, which can actively reduce cholesterol.
The Healthiest Way to Make Dietary Changes
Making major diet and lifestyle changes can be daunting. It can be helpful to start by switching out one unhealthy food at a time. You can then make further changes as your body and habits adjust.
Keep in mind that small positive changes are better than no changes at all.