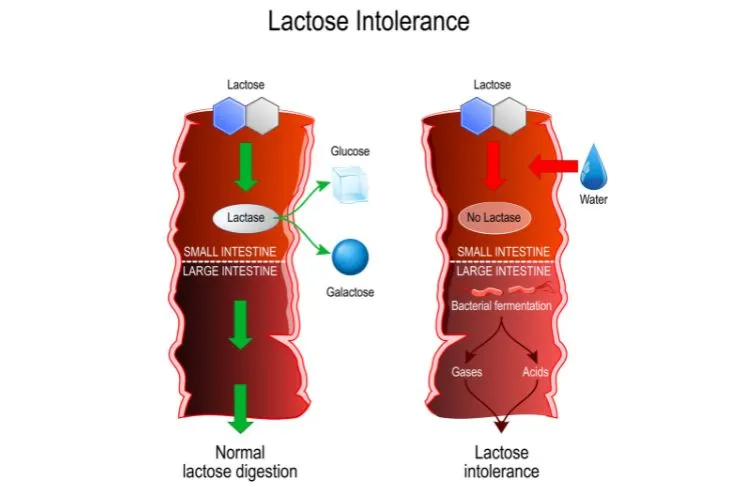
- Lactose intolerance is when the body is unable to break down or digest lactose, the sugar found in milk and milk products.
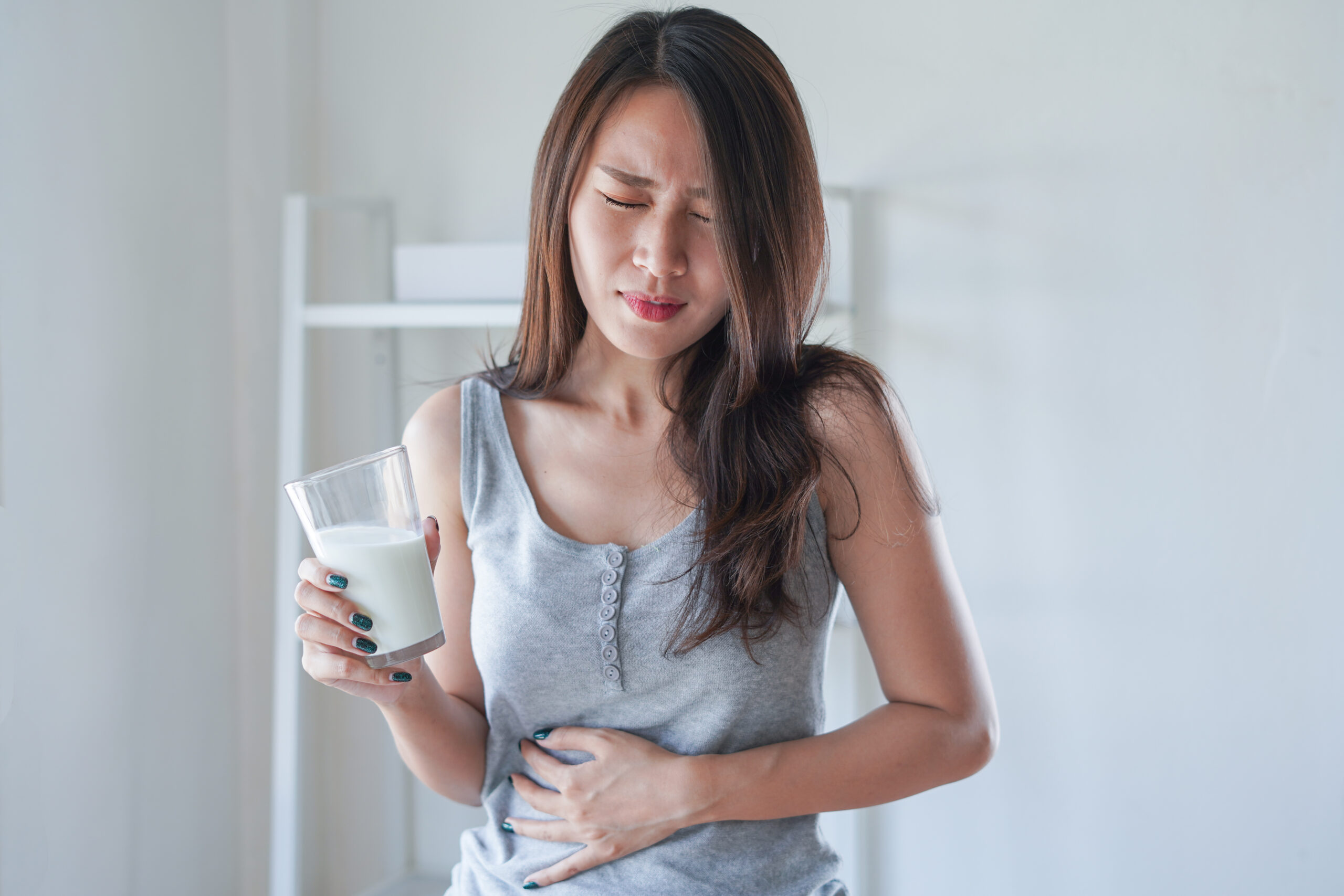
- People who are lactose intolerant will experience bloating, gas, nausea, and abdominal pain when they consume dairy products.
- The most common cause of lactose intolerance is age. It can also be from a digestive disorder, genetics, or present at birth (particularly in premies).
- Most effective form of treatment for lactose intolerance is to avoid/limit dairy products, take an enzyme pill, and supplement with non-dairy products.
For many people, dairy products like cheese are among their favorite foods to eat. Let’s face it, some of our most desired guilty pleasures come with cheese! Unfortunately, it can also be our greatest enemy — at least when it comes to digestion.
Ever had an uncomfortable rumbling in your stomach shortly after eating dairy? If so, it’s quite possible you are lactose intolerant. According to the Cleveland Clinic, it’s estimated that 68-percent of the world population have some degree of lactose intolerance. To get better informed on the topic, here’s a look at everything to know about lactose intolerance, including the symptoms, causes, and treatment options…
What is Lactose Intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is when the body is unable to break down or digest the sugar found in milk and milk products. This sugar is called lactose, says John Hopkins Medicine. It occurs when the small intestine doesn’t produce enough lactase, a digestive enzyme needed to break down the lactose so that the body can absorb it.
“People who are lactose intolerant have unpleasant symptoms after eating or drinking milk or milk products,” writes the source. These symptoms include bloating, diarrhea, and gas.
Lactose Intolerance vs. Dairy Allergy
People sometimes confuse a lactose intolerance with a dairy allergy, but the two are very different. A person with an allergy to dairy cannot consume any dairy products, whereas someone with a lactose intolerance can likely consume dairy in varying amounts. “With dairy allergy, the immune system works to fight the proteins in milk, even though they are not inherently harmful,” writes VeryWell Health.
The symptoms are another big difference. Unlike the discomfort associated with a lactose intolerance, dairy allergies can be life-threatening. If you or a child has an allergic reaction to a dairy product, you should go to the hospital immediately. “Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, itching or tingling of the lips, hives, wheezing or coughing, and shortness of breath” are all symptoms of a dairy allergy, warns VeryWell Health.
Symptoms
Symptoms of lactose intolerance vary based on the person. Most of the time symptoms appear between 30-minutes to 2-hours after consuming food or drinks containing lactose. John Hopkins Medicine lists the following as the most common symptoms associated with lactose intolerance:
- Belly (abdominal) cramps and pain
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea
The severity of these symptoms will depend on how much lactose the person ingested and how much lactase their body makes, explains the source. If you haven’t been diagnosed with lactose intolerance, it can be hard to identify because the symptoms resemble those of other health problems. Talk to a doctor to make sure.
Causes
The cause behind lactose intolerance is a shortage of lactase in the body, explains the Mayo Clinic. Lactase is an enzyme the small intestine produces to digest lactose.”Normally, lactase turns milk sugar into two simple sugars — glucose and galactose — which are absorbed into the bloodstream through the intestinal lining,”writes the source.
People who are lactase deficient, lactose from the food moves into the colon instead of being processed and absorbed. When it enters the colon, normal bacteria interacts with undigested lactose, which then causes symptoms to occur. There are three main types of lactose intolerance, each have different causes and risk factors.
Primary Lactose Intolerance
The most common type is primary lactose intolerance which occurs as a result of age. According to WebMD, most peoples body stops making lactase by the age of 5 (can be as early as 2) which means we lose the ability to absorb lactose over time. The less lactase there is in the body, the harder it is to digest dairy products.
Healthline notes this type of lactose intolerance may be genetic since it’s seen in some populations more than others. “It’s caused by genes and is common among people of an African, Asian, Hispanic, Mediterranean, and southern European background,” writes WebMD.
Secondary Lactose Intolerance
Secondary lactose occurs as a result of another condition that affects the small intestine where lactase is produced. “This is because inflammation in the wall of your gut may lead to a temporary decline in lactase production,” writes WebMD.
For example, some digestive diseases (i.e. Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease), stomach or intestinal infections, and injuries to the small intestine (i.e. surgery, trauma, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy) can reduce the amount of lactase in the small intestine. WebMD says the two most common intestinal diseases linked to low lactase are Crohn’s disease and celiac disease.
Congenital or Developmental Lactose Intolerance
The last two types of lactose intolerance are congenital and developmental lactose intolerance. Developmental lactose happens to babies who are born prematurely. In most cases, this form of lactose interlace will go away over time. It typically lasts for a short time after birth, says WebMD.
WebMD reassures that congenital lactose intolerance is extremely rare. This occurs when there is very little or no lactase at all in the small intestine right from birth. It is a genetic disorder which means both parents have to have the gene in order for it to pass onto the child.
Risk Factors
According to the Mayo Clinic, there are several risk factors that make a person more likely to be lactose intolerant. The first risk factor is age. Lactose intolerance usually shows up in adulthood and is somewhat uncommon in children and babies. Ethnicity is also a risk factor. Lactose intolerance is more common in people of African, Asian, Hispanic, and American Indian descent, says the source.
Other factors are premature birth. “Infants born prematurely might have reduced levels of lactase because the small intestine doesn’t develop lactase-producing cells until late in the third trimester.” People who have a disease that affects the small intestine are also more likely to be lactose intolerant. This includes Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and bacterial overgrowth.
Lastly, certain cancer treatments, particularly radiation therapy in the stomach or any intestinal complications from chemotherapy can increase a person’s risk for being lactose intolerant.
Diagnosis
If you suspect you are lactose intolerant, your doctor will likely ask you to refrain from consuming milk and dairy products for one or two weeks to see if your symptoms subside, says the Cleveland Clinic. The next step is to perform a hydrogen breath test which works to measure the amount of hydrogen in the breath after drinking a lactose-loaded beverage. If there’s a high level of hydrogen, that indicates a lactose intolerance.
A doctor can also perform a lactose tolerance test which is done through a blood test. “The person consumes a lactose solution, and a physician. takes blood samples to measure their glucose levels,” explains Medical News Today. “If blood glucose levels remain the same, the body has not broken down the lactose properly.” Lastly, if the first two tests are not suitable, they can also perform a stool test checking for high levels of acetate and other fatty acids.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there isn’t one form of treatment to cure or make a body more lactase. The best form of treatment is to manage symptoms by changing your diet. In the past, people who were lactose intolerant were told to avoid dairy products. According to John Hopkins Medicine, today health experts recommend people try different dairy products to find out which ones cause fewer symptoms. This ensures they get some calcium and other important nutrients.
Other tips to manage symptoms would be to eat milk and milk products with other foods. “You may find you have fewer symptoms if you take milk or milk products with your meals,” writes the source. Eat dairy products with lower levels of lactose, such as hard cheese and yogurt. Look for lactose-free and lactose-reduced milk and milk products. You can also inquire about taking a lactase pill or lactase drops when eating or drinking milk products, says John Hopkins Medicine.
If you’re struggling to find dairy products that don’t cause symptoms, talk to your doctor or a dietician. They can help suggest foods to ensure you’re getting enough calcium and other nutrients.
Foods That Trigger Lactose Intolerance
Milk and dairy are the most well-known lactose foods, but according to WebMD there are others. “Some nondairy products have a protein called casein, which can have traces of lactose,” writes the source. Read food labels carefully. Look for the following ingredients which all contain lactose: curds, dry milk solids, milk, milk byproducts, dry milk powder, and whey.
If you’re highly sensitive to lactose, WebMD advises avoiding the following: baked goods, bread, baking, and pancake mixes, breakfast cereals, margarine, instant foods, some candy (milk chocolate), nondairy creamers, nondairy whipped topping, processed meats, protein and meal replacement bars, and salad dressing.
Lactose-Free Alternatives
Most of us grew up learning that we needed to drink our milk in order to grow strong bones. And that’s true! Dairy is an important source of nutrients like calcium, protein, vitamin A, B12, and D. However, if you’re lactose intolerant, you’ll need to get these nutrients elsewhere. Luckily, there are many alternatives to dairy products, including soy milk, almond milk, and alternative cheeses that are reinforced with vitamins, says Medical News Today.
Some of the best dairy-free sources of calcium are seaweed, nuts and seeds, beans, oranges, figs, quinoa, collard greens, broccoli, kale, and okra. You can get vitamin A from carrots, broccoli, sweet potatoes, cod liver oil, liver, spinach, pumpkin, cantaloupe, melon, egg, apricot, mango, and peas. The same source also lists fatty fish, egg yolk, fish liver oils, and some fortified plant milks as a good food source for vitamin D.
To ensure you’re eating a well-rounded diet, talk to a doctor or dietician before making any significant dietary changes.
 Shutterstock/Evan Lorne
Shutterstock/Evan Lorne