Most people have heard of scoliosis, or perhaps even know somebody who has it. Scoliosis is a condition that often develops in childhood where the spine curves rather than appearing straight up and down. While this condition is fairly common and treatable, it’s imperative to catch it early on. That way, it won’t progress and cause further discomfort.
While mild scoliosis cases can be treated through external methods, such as bracing and physical therapy, more severe instances need additional medical interventions, such as definitive fusion or vertebral body tethering. While the condition is centralized to the spine, it can impact the body in various ways. Many parts of the body are dependent on the vertebral column, from the surrounding joints to the abdominal organs. The body is interconnected, which means scoliosis can come into play all over.
The Spinal Curve
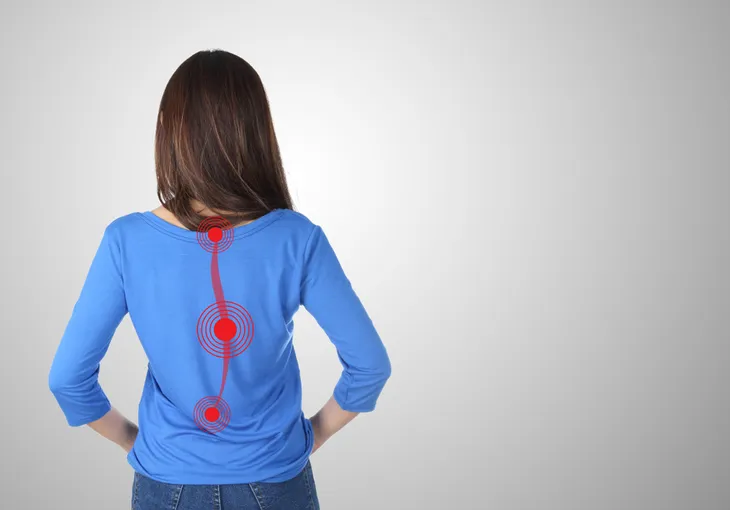
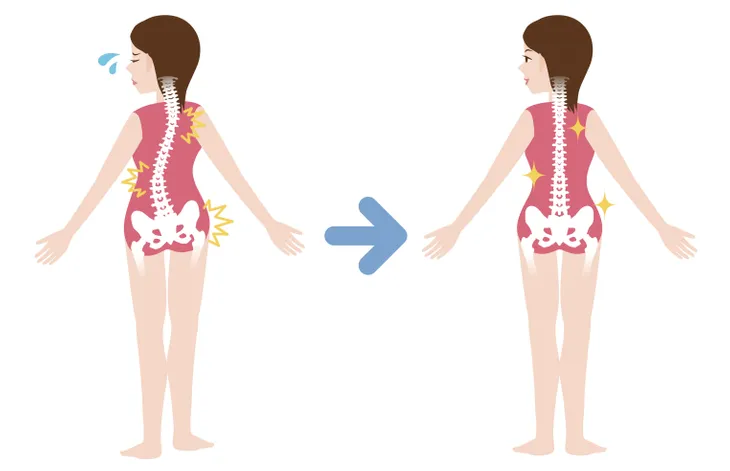
The most obvious way that scoliosis affects the human body is through the spinal curve itself. Usually, the curve will appear in the center of the spine and cause the shoulders, waist, and back to appear uneven. Sometimes, one shoulder blade or hip will appear more prominent than the other one.
Scoliosis spinal curves are often referred to as either a C curve or an S curve, which is based on the shape and severity. These shapes can appear subtly or much more severely, depending on each unique case. S curves are often referred to as double curves, due to the additional turn they create in the spine.
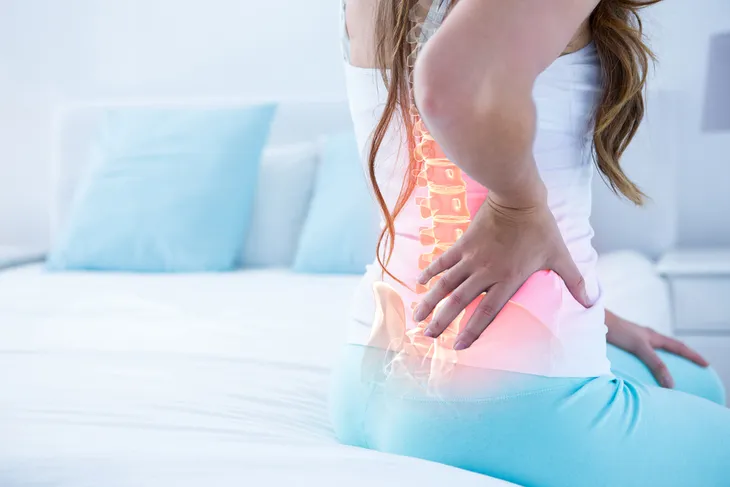
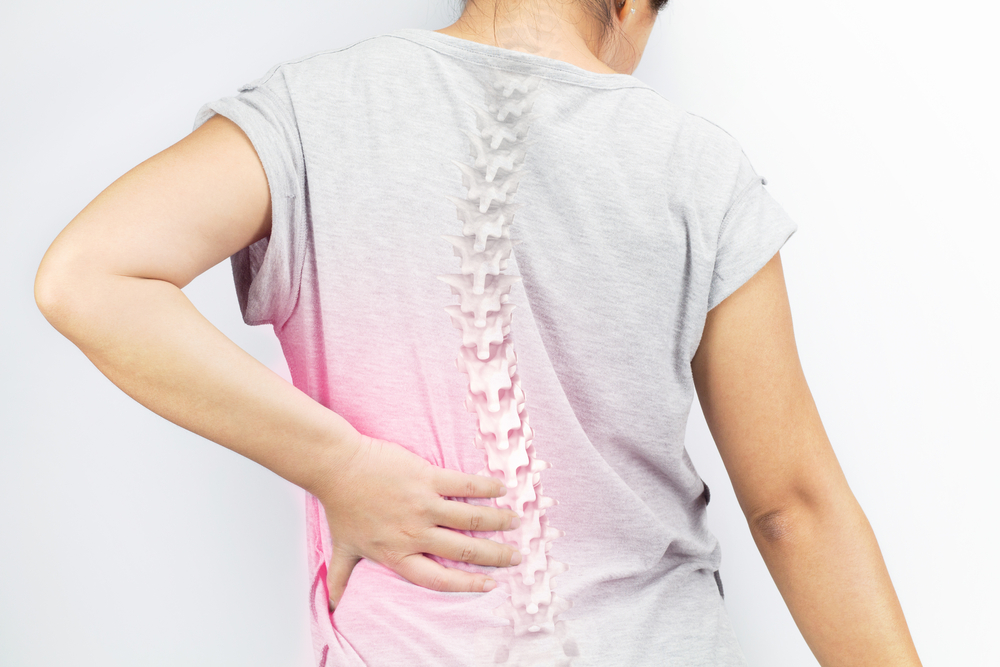
Back Pain
While this may not come as a shock, scoliosis and the spinal curve associated with it can cause back pain or even reduce range of motion, especially if it goes untreated. While the spine is strong, it is also sensitive. If things like bad posture or sitting too long can cause back pain, an unnatural curve of the spine certainly can too.
Some people with scoliosis don’t experience as much pain as others, and it often goes on a case-by-case basis. Usually, treatment will help relieve pain and discomfort and help bring back any range of motion that was previously lost.
The Rest of the Skeletal System
In the most literal sense, abnormalities of the spine even a slight curve, could throw other bones and joints out of balance. Often, patients with scoliosis will report pain tin the neck, knees, hips, shoulders, and legs. Scoliosis can also affect central bones, such as the ribs and cause shifts in the pelvis.
Every case is different, and the adverse effects will depend on the severity of the curvature. The stronger the curve is, the more likely it is to shift other bones and joints within the body.
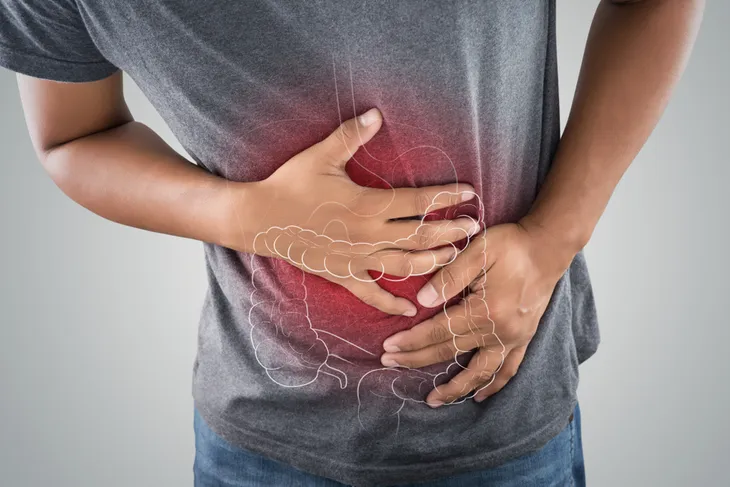
Digestive Issues
Although scoliosis is a condition that centralizes in the skeletal system, it can unfortunately impact other organs if left untreated, especially in more severe cases. Curves in the spine can cause digestive problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), heartburn, acid reflux, and abdominal pain. This is because the spinal column supports the organs of digestion, and there are many points of contact within it.
The spine is responsible for relaying messages to and from the brain, and when that system is compromised, it can cause miscommunication. It also offers structural support and coordination of reflexes, which are all difficult to do when there is spinal curvature.
Respiratory Issues
Similarly to how a curve in the spine can impact the digestive system, it can also affect the lungs, causing breathing issues. Scoliosis can sometimes shift the chest wall and restrict lung size, which is often called a restrictive lung defect.
While this isn’t present in all cases, it’s a possibility. This is especially the case if it becomes difficult to breathe (shortness of breath is common) or breathing becomes painful.
Cardiovascular Issues
Another internal organ that can suffer when the spine is curved is the heart, as well as the cardiovascular system in general. In severe cases of scoliosis, the spinal curvature can cause the ribcage to press against the heart. This can make it harder for this organ to pump and send blood to the rest of the body. Often, lung and heart issues can come together in severe scoliosis cases, although this isn’t always the case.
Fatigue
As a result of skeletal, muscular, and organ strain, some people with scoliosis experience fatigue over time. While it can result from one specific complication, such as back pain or respiratory issues, it can sometimes occur due to a combination of multiple symptoms. Multiple sources at play could cause anybody to feel drained and tired, let alone just one malfunctioning system.
Progression
Scoliosis is not a condition that can be left untreated. Even mild cases that can be managed with external treatment should be handled by medical professionals who specialize in spinal care.
If scoliosis is not addressed, it can cause back problems, overall skeletal dysfunction and more severe cardiovascular and breathing issues. While the type of treatment necessary will depend on the severity of the curvature, it’s important to address scoliosis with a doctor, ideally as early as possible, so the condition does not progress.
Treating the Curve
Regardless of the severity of scoliosis, it’s essential to see a physician. The earlier you catch scoliosis and find the proper treatment, the less it will progress. Nobody deserves to be uncomfortable in their spine, especially when there are so many ways to treat the curve.