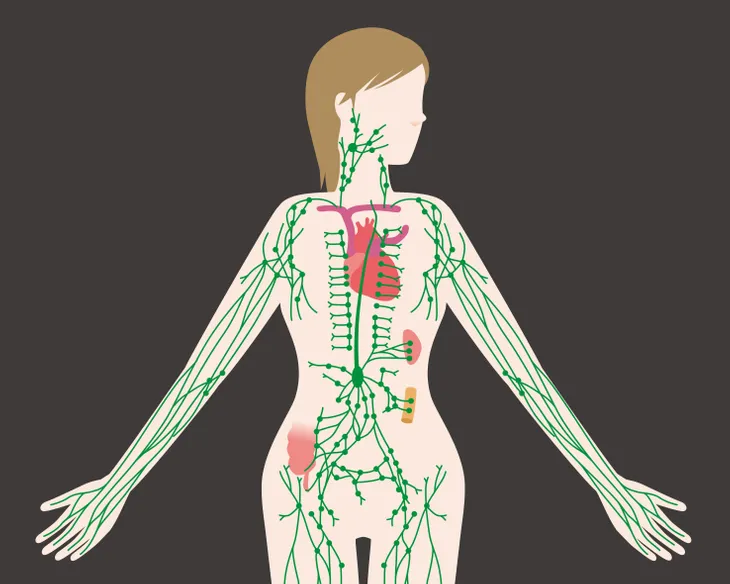
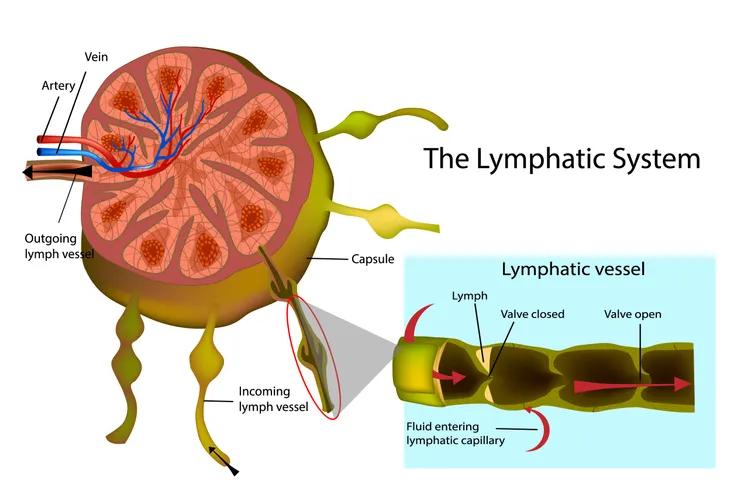
Lymphedema is a condition where the extremities become swollen as a result of damage to the body’s lymphatic system—particularly the lymph nodes. The lymphatic system, a part of the immune system, is “a network of vessels that course throughout the body to collect excess fluid as well as waste products,” defines eMedicineHealth.com.
Because these excess fluids and waste products are filtered through the lymph nodes, if they become damaged, it can lead to a buildup in various parts of the body, resulting in swelling. There are a variety of factors that can cause this damage, which we’ll discuss below, along with the most common symptoms of lymphedema to be mindful of.
Causes of Primary Lymphedema
1. Congenital Lymphedema
Primary lymphedema is rare and happens as a result of genetic mutations that cause the lymph vessels to develop improperly, “undermining its ability to drain fluid properly,” says MedicalNewsToday.com.
Congenital lymphedema is one such cause of primary lymphedema and is present at birth. It is “more common in females, and accounts for about 20-percent of all cases of primary lymphedema,” says MedicineNet.com. The source adds that there is a subtype of congenital lymphedema as well, termed Milroy disease, where the condition occurs as a result of genetic inheritance.
2. Lymphedema Praecox (Meige Disease)
The most common cause of primary lymphedema is lymphedema praecox—also known as Meige disease—and is defined as “lymphedema that becomes apparent after birth and before the age of 35, and symptoms most often develop during puberty,” says MedicineNet.com.
The source also indicates that females are four times more likely to develop it than males. And while it most commonly becomes evident during puberty, it’s possible that it may also (or only) occur during pregnancy.
3. Lymphedema Tarda (Late-Onset Lymphedema)
An even rarer cause of primary lymphedema is lymphedema tarda, or late-onset lymphedema. The type gets its name because of when it occurs in a person’s life, typically after the age of 35.
Whereas both congenital lymphedema and lymphedema praecox primarily affects females, the National Lymphedema Network indicates that lymphedema tarda “usually affect both lower extremities in men and women.”
Causes of Secondary Lymphedema
4. Surgery
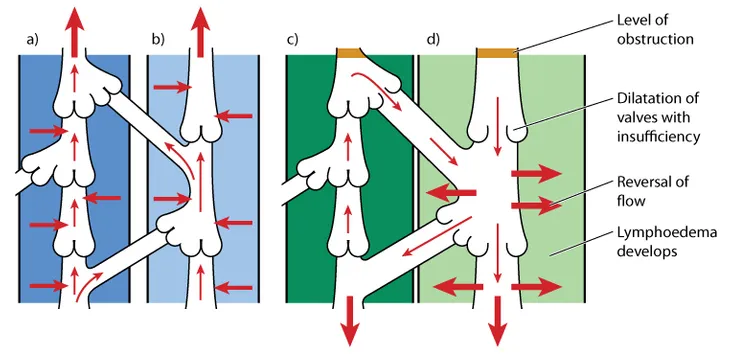
Secondary lymphedema is far more common than primary lymphedema, and occurs “when a normally-functioning lymphatic system is blocked or damaged,” says MedicineNet.com. A variety of factors can cause a blockage or damage, including surgery.
For example, the Mayo Clinic says, “Lymph nodes may be injured in surgery that involves blood vessels in your limbs.” Or, in the case of surgery to treat breast cancer (the most common cause of lymphedema in the United States), the lymph nodes may be removed altogether to stop it from spreading.
5. Cancer or Radiation Therapy for Cancer
It’s not just cancer-treating surgery that can cause lymphedema to occur. Radiation therapy, while effective at destroying cancer cells, “can sometimes damage nearby healthy tissue, such as the lymphatic system,” leading to lymphedema, says MedicalNewsToday.com.
The Mayo Clinic adds that the cancer cells themselves can “block lymphatic vessels,” resulting in lymphedema. “For instance,” the source says, “a tumor growing near a lymph node or lymph vessel could enlarge enough to block the flow of the lymph fluid.”
6. Infection
Secondary lymphedema can also occur because of bacterial infections, fungal infections, or parasites that cause inflammation or damage to the lymph nodes, restricting the proper drainage of the lymph fluid.
Severe cellulitis, for example, “may damage tissue around the lymph nodes or vessels,” says MedicalNewsToday.com and can lead to scarring that increases the risk of lymphedema. Infection-related lymphedema isn’t a major concern in North America, although, as the Mayo Clinic indicates, it is “…most common in tropical and subtropical regions and is more likely to occur in developing countries.”
Symptoms
7. Swelling in the Arms or Legs
When it comes to the symptoms of lymphedema, swelling in various areas of the body is the primary one to be mindful of. MedicalNewsToday.com indicates that it may occur in “either a part or the whole leg or arm, including the fingers or toes.”
At early onset, the NHS says the swelling “may come and go…getting worse during the day and going down overnight.” Without proper treatment, however, it is likely to become “more severe and persistent” over time.
8. Feeling of Heaviness or Tightness in Affected Limb
Although swelling in the extremities is the primary symptom of lymphedema, it is not necessarily the first to occur. According to MedicineNet.com, “Mild lymphedema first may be noticed as a feeling of heaviness, tingling, tightness, warmth, or shooting pains in the affected extremity.“
The source adds that such symptoms “may be present before there is obvious swelling of an arm or leg” and can sometimes be accompanied by tightness in the joints, making them hard to move.
9. Difficulty Fitting Into Clothes and Wearing Jewelry
Along with feelings of heaviness or tightness in the affected areas, someone with lymphedema may also notice early on in the condition that they suddenly have a hard time fitting into their clothes or shoes.
Additionally, they may have difficulty wearing items such as watches, rings, and bracelets, finding them too tight against their skin. This is due to mild swelling of the limbs, which can be hard to detect early on with lymphedema.
10. Restricted Range of Motion
Experiencing restricted range of motion is another common symptom of lymphedema. In some cases, it may be a result of tightness in the joints, which can cause affected individuals to have reduced flexibility.
Alternatively, range of motion can also be restricted due to swelling in the extremities, a common symptom of lymphedema that was mentioned earlier. Regardless of the cause, not being able to move the limbs as normal can impact a person’s day-to-day life by making it difficult to engage in exercise or other regular activities.
11. Recurring Infections
People with lymphedema tend to be prone to frequent and recurring infections, particularly of the skin. The National Lymphedema Network explains that this is because when lymph fluid becomes trapped within the body (as a result of damaged lymph nodes), it is “a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria.”
This can be particularly dangerous for those who have had their lymph nodes removed, as the source says, “…[I]nfections can progress rapidly and can be severe by the time they are detected.”
12. Hardening and Thickening of the Skin (Fibrosis)
Another common symptom of lymphedema is fibrosis, where the skin in the affected area thickens and hardens. In some cases, MedicineNet.com indicates it may even “take on a lumpy appearance described as an orange-peel (peau d’orange) effect.”
Additionally, the source says, “The overlying skin can also become scaly and cracked, and secondary bacterial or fungal infections of the skin may develop.” Other skin symptoms to look out for include tightness, warmth, redness, itchiness, blisters, wart-like growths, or skin that doesn’t indent when you press on it.