Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, will affect about 53,000 people in the United States this year. While most people diagnosed with this type of cancer are over 60-years-old, it can develop in young people too. It’s also twice as common in men as in women. The good news is that mouth cancer has a survival rate of about 70 to 90-percent but only if it’s detected early.
If cancer progresses and has spread to other parts of the body, the survival rate drops to 38-percent. This is why learning the warning signs and risk factors is so important. Follow along as we uncover the signs, symptoms, and treatment options of mouth cancer, and make sure you speak to your doctor if you think you’re at risk.
What is Mouth Cancer?
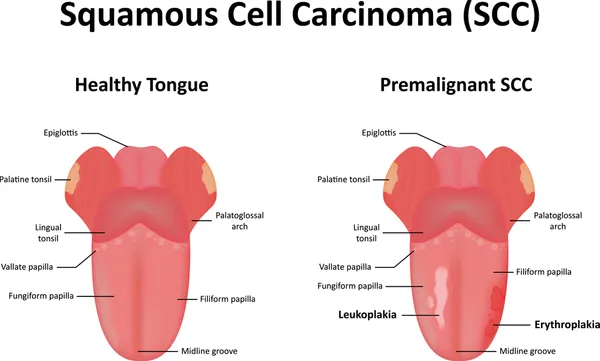
Mouth cancer is cancer that develops in any part of the oral cavity. Mouth cancer can occur on the tongue, gums, roof of the mouth, floor of the mouth (below the tongue), the inner lining of the cheeks, and on the lips.
When cancer develops inside the mouth, it’s often referred to as oral cancer. Furthermore, while this might be less common, tumors can also develop on the tonsils at the back of your mouth, the part of your throat that connects your mouth to the windpipe, and in the glands that produce saliva.
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
There are several warning signs and symptoms of mouth cancer that you should be on the lookout for. Common signs and symptoms of mouth cancer include:
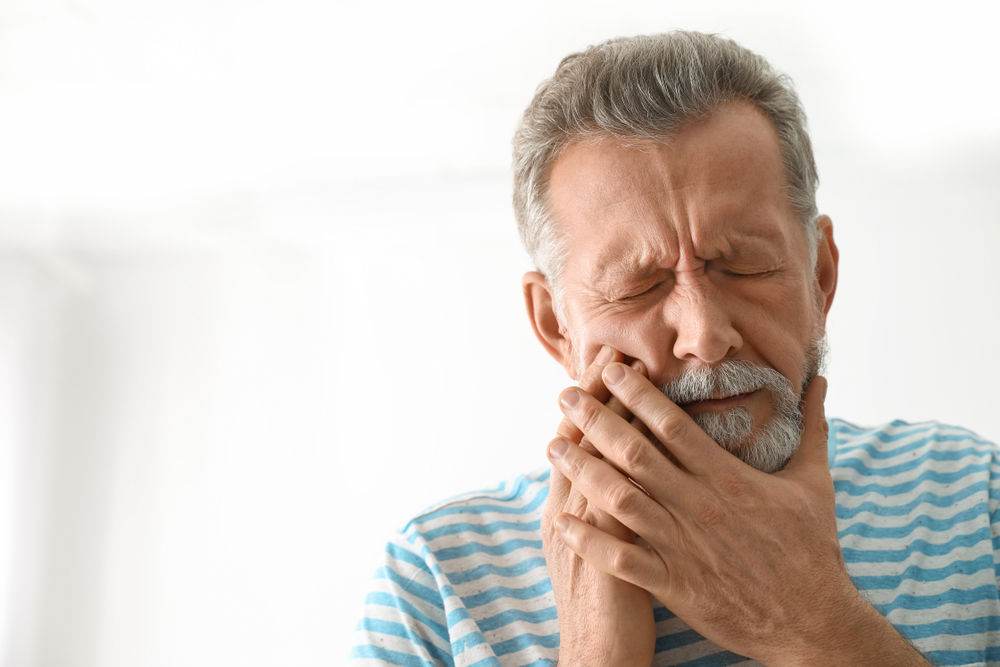
- Mouth and/or ear pain
- Unexplained loose teeth
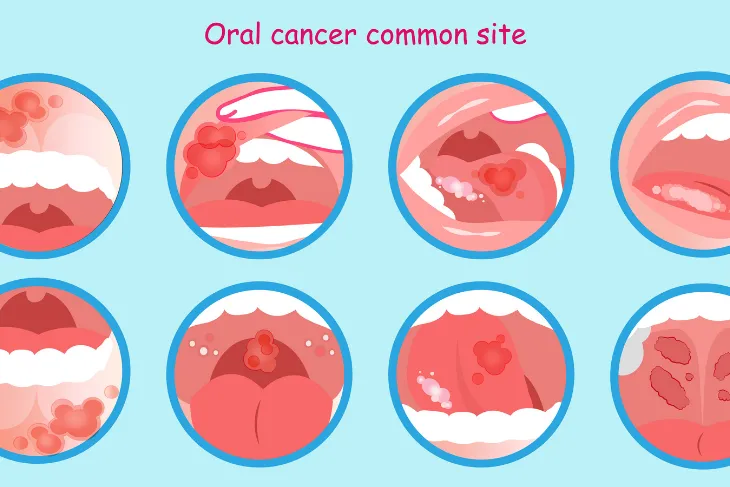
- A white or red patch on the inside of your mouth
- Mouth ulcers that are painful and don’t heal
- Lumps in the mouth or on the neck that don’t go away
- Difficulty swallowing or pain when swallowing
- Changes in speech.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms and they do not clear up on their own after a few weeks, make sure you speak with your dentist or doctor.
Causes of Mouth Cancer
Mayo Clinic explains, “Mouth cancers form when cells on the lips or in the mouth develop changes (mutations) in their DNA.” When mutations develop, this tells the cells to continue to grow and divide whereas if they were healthy, the cells would be told to stop growing and die. As the abnormal cancer cells accumulate, they can form a tumor and over time they can spread inside the mouth, as well as to other areas of the neck and head.
Unfortunately, there isn’t any concrete evidence that explains what causes the mutations that lead to mouth cancer. That being said, doctors have identified several factors that can increase your risk of developing mouth cancer.
Risk Factors
There are several factors that can put you at a greater risk for developing mouth cancer. These risk factors include excessive alcohol consumption, excessive sun exposure to your lips, a weakened immune system, and a sexually transmitted virus called human papillomavirus (HPV).
You’ll also be at risk if you use tobacco of any kind, which includes cigarettes, cigars, chewing tobacco, pipes, etc. If you want to reduce your risk of developing mouth cancer, you’ll want to stay away from these risk factors.
Diagnosing Mouth Cancer
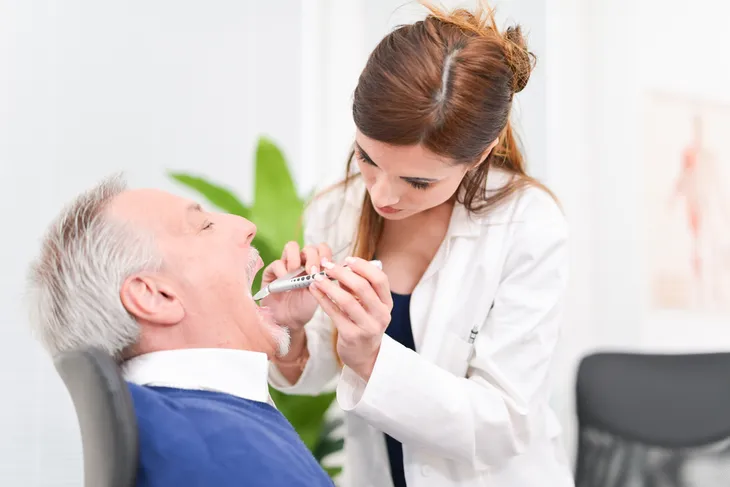
If your doctor or dentist suspects that you might have mouth cancer, there are a couple of tests and procedures they can use to diagnose cancer. First, they’ll perform a physical exam. Your doctor or dentist will examine your mouth and will be on the lookout for any abnormalities.
If there is cause for concern, your doctor may remove a sample to send it for laboratory testing, which is called a biopsy. To collect the sample, your doctor may use a needle to remove a sample or they might cut a sample from your mouth. Once the sample is sent away it can be tested for cancerous cells.
Treatment Options
If it is confirmed that you do have mouth cancer, there are several treatment options available. The treatment will depend on the location and stage of your cancer, as well as your overall health.
Some patients require just one type of treatment, while others may need a combination of treatments. Follow along as we explore the different types of treatments available and make sure you discuss your options with your doctor.
Surgery
One of the treatment options for mouth cancer is surgery. For smaller cancers, your surgeon may perform surgery to remove the tumor, as well as a bit of the healthy tissue around it to ensure all of the cancer cells have been removed. That being said, large tumors may require a more invasive surgery, such as removing a portion of your tongue.
Furthermore, your surgeon may need to remove cancer that has spread to your neck. If cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, they may need to remove the lymph nodes and associated tissues in your neck.
Finally, your surgeon may need to perform surgery to reconstruct your mouth after removing your cancer. Keep in mind that surgery to remove this type of cancer can often affect your ability to speak, eat, and swallow, as well as your appearance.
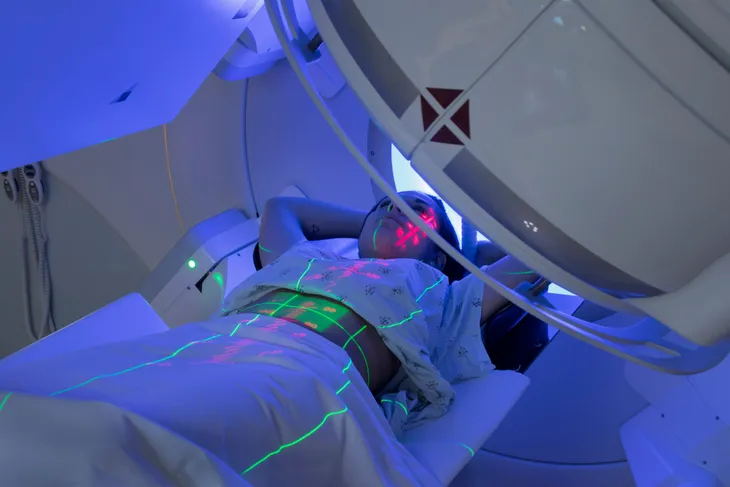
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a type of treatment that uses beams of intense energy to ward off cancer cells. Mayo Clinic explains, “Radiation therapy damages cells by destroying the genetic material that controls how cells grow and divide.”
This type of treatment is often used after surgery; however, it may also be used on its own, especially if you have early-stage mouth cancer. Radiation therapy may also be combined with chemotherapy to increase the effectiveness of the treatment. That being said, combining the two treatments may increase their side effects. Some side effects of radiation therapy include tooth decay, damage to your jawbone, and dry mouth.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The American Cancer Society explains, ” For oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers, the drugs are given into a vein or taken by mouth, which allows them to enter the bloodstream and reach cancer that has spread throughout the body.”
Chemotherapy is often combined with other cancer treatments, such as radiation therapy and/or surgery. Chemotherapy drugs may even increase the effectiveness of radiation therapy, which is why they are often combined. The side effects of this treatment will vary depending on the drugs you receive. That being said, some common side effects include hair loss, nausea, and vomiting. You can ask your doctor which side effects to expect.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Another form of treatment for mouth cancer is targeted drug therapy. This treatment uses drugs to target specific genes and proteins that are in charge of the growth and survival of cancer cells.
Targeted drug therapy can be used alone or doctors may use it along with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. One of the cancer drugs used for mouth cancer is cetuximab, also known as Erbitux. This drug quickly destroys cancer cells and is administered as an IV drip into your bloodstream. Make sure you speak to your doctor to find out if targeted drug therapy is a good treatment option for you.
Immunotherapy
Finally, another way to treat mouth cancer is through immunotherapy. The American Cancer Society explains, “Immunotherapy is treatment that uses certain parts of a person’s immune system to fight diseases such as cancer.” This type of treatment is often reserved for patients with advanced mouth cancer that are not responding to other types of treatment.
Immunotherapy can be used in a couple of ways. First, it can stimulate or boost your immune system, helping it to work harder at attacking unhealthy cancer cells. The second way is by creating substances in a lab that act as immune system components and using them to help enhance how your immune system works to attack unhealthy cancer cells.
Preventing Mouth Cancer
While there is no proven way to prevent mouth cancer, there are lifestyle changes you can make to reduce your risk of developing it. If you use tobacco, it’s time to quit, and if you don’t use it, make sure you don’t start.
Next, you may want to stop drinking alcohol entirely or at the very least drink it in moderation. You should also limit sun exposure to your lips or at the very least wear sunscreen on your lips when you’re outside. Finally, make sure you visit your doctor or dentist regularly so they can inspect your mouth at every visit.