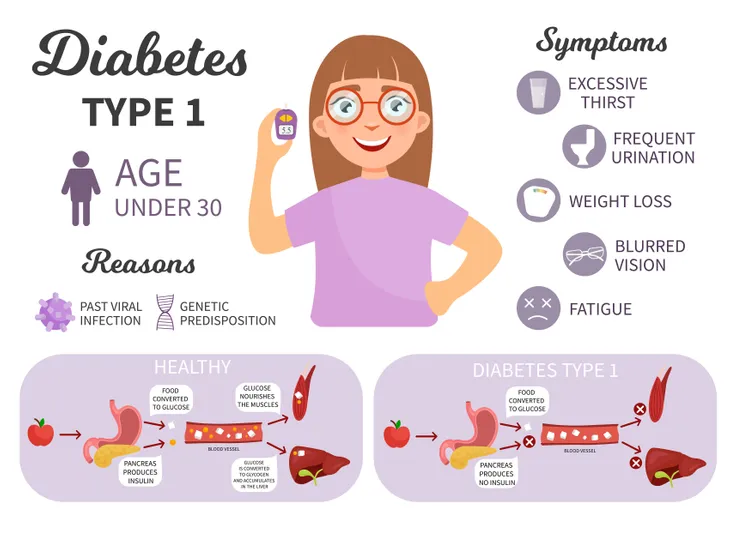
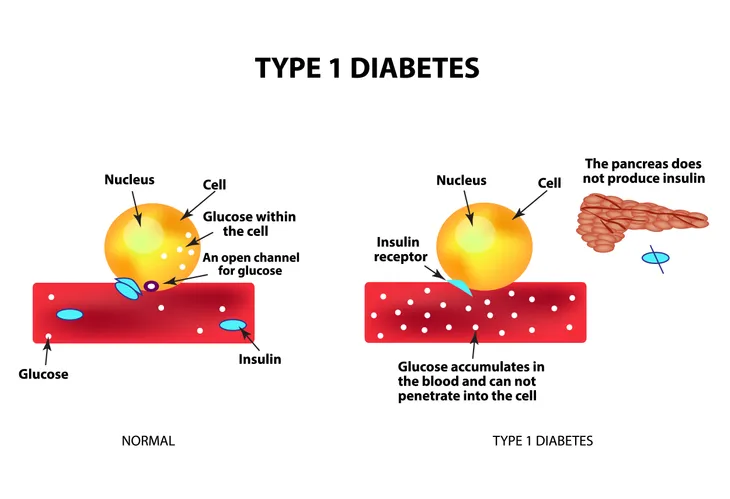
Type 1 diabetes, sometimes known as juvenile diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects millions of people. It is the result of your body’s own immune system mistakenly destroying the beta cells in the pancreas causing an inadequate production of the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood.
While glucose is required by your body as a main source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and other tissues, the buildup of glucose in your bloodstream instead of the absorption of glucose by your cells, as happens to type 1 diabetics, has potentially life-threatening effects. If you’d like to learn more about this condition, let’s take a moment to learn about the common signs and symptoms…
Want diabetes content delivered straight to your inbox? Sign up for our Diabetes newsletter and receive exclusive news and articles written from our team of diabetes experts.
Complications
Left untreated, type 1 diabetes can lead to such life-threatening complications as:
- Heart and blood vessel disease
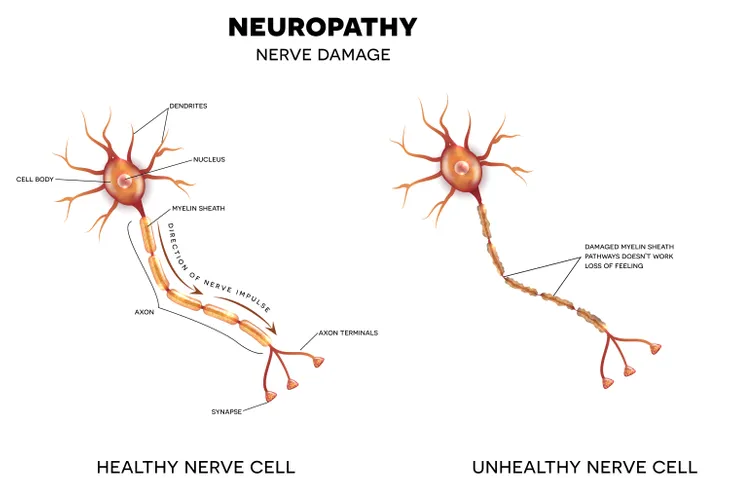
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
- Eye damage
- Foot damage
- Skin and mouth conditions
- Pregnancy complications
While nearly 30 million people suffer from diabetes in the United States, only 1.25 million of those people have type 1 diabetes – about 5-percent. It also tends to affect males and females equally. Unfortunately, there is neither a known form of prevention nor a cure for type 1 diabetes. There is, however, an effective form of treatment in the form of managing blood sugar levels with a prescribed hormone that allows your body to use glucose for energy.
Can Be Difficult To Recognize
While the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes can begin to show quite early, there are three things that make recognizing type 1 diabetes difficult. The first is that many of the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes are shared with other, more common, less dangerous illnesses. The second is that the signs and symptoms can be very subtle. The third is that the process inside your body that causes type 1 diabetes can take months or even years to occur.
This is why it’s important to take notice of any changes in your body and get checked by your doctor at the first sign of anything that could even remotely be related to type 1 diabetes.
Common Signs and Symptoms
To help you understand what to watch out for, the signs and symptoms associated with type 1 diabetes can include:
- Excessive urination or bed-wetting in children (the result of your kidneys trying to expel excess sugar in your blood)
- Feeling very thirsty, experiencing a dry mouth, or having itchy skin (due to the dehydration caused by your kidneys trying to expel excess sugar in your blood)
- Feeling very tired or weak, increased hunger (especially after eating), unintended weight loss, or loss of muscle bulk (due to your body not getting adequate energy from the food you eat)
- Frequent or recurring infections, slow-healing cuts or bruises, tingling or numbness in the hands or feet, or difficulty getting or maintaining erections in men (due to high blood sugar levels affecting blood flow and causing nerve damage, which in turn makes healing difficult)
- Frequent yeast infections (due to yeast infections feeding on glucose)
- Blurred vision (due to the lens of your eye changing shape)
Severe Signs and Symptoms
In more serious cases of type 1 diabetes, signs and symptoms can include:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
- Low body temperature (below 97º F)
- Rapid, heavy, labored breathing (sometimes called Kussmaul respiration)
- Stomach pain
- Shaking and confusion
- Fruity, potentially pear-smelling breath (due to high ketones, a result of ketoacidosis)
- Loss of consciousness (this is rare)
- Changes to (or loss of) menstruation in women
- Reduced blood pressure (falling below 90/60)
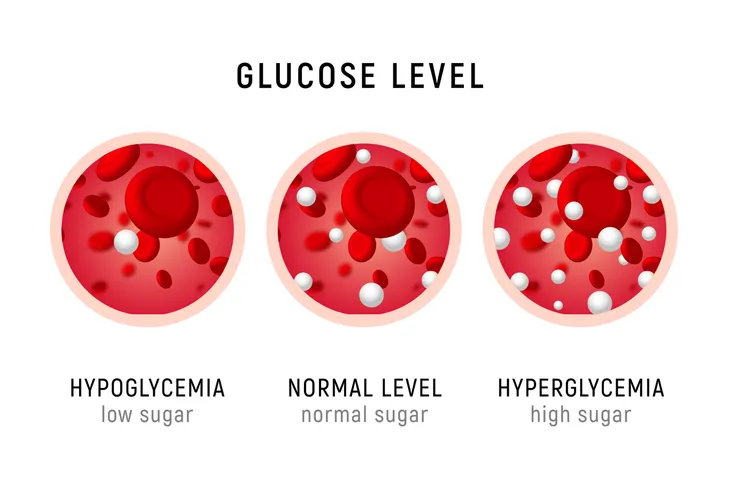
- Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose)
- Hyperglycemia (high blood glucose)
If you experience any of these signs or symptoms, you should seek immediate medical attention.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, for example, happens when your blood glucose levels become very low. Although it is usually a result of taking too much of the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood, the most common form of treating type 1 diabetes, this in itself can produce potentially life-threatening symptoms.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
The signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
- feeling shaky and irritable
- sweating
- tingling lips
- feeling weak
- feeling confused
- hunger
- nausea (feeling sick)
Left uncontrolled, hypoglycemia can cause confusion, slurred speech and, eventually, unconsciousness. Fortunately, all that is usually required to bring hypoglycemia back under control is to eat something sugary.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, on the other hand, is the result of your body’s inability to produce an adequate amount of the hormone that allows your body to use glucose for energy, which causes your blood glucose levels to become dangerously high. While they tend to come on more severely, the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia are similar to those of type 1 diabetes and can include:
- extreme thirst
- a dry mouth
- blurred vision
- drowsiness
- a need to pass urine frequently
Without the proper treatment, hyperglycemia can lead to what’s called diabetic ketoacidosis – a life-threatening condition where the body breaks down fat and muscle as an alternative source of energy. This breakdown can cause a build-up of acids in your bloodstream, which can cause vomiting, dehydration, unconsciousness and even death.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, there is neither a known form of prevention nor a cure for type 1 diabetes. However, on the bright side, the symptoms of type 1 diabetes can usually be managed by taking prescribed doses of the hormone that allows your body to use glucose for energy.
While type 1 diabetes is certainly less common than its sibling, type 2 diabetes, the severity of symptoms associated with type 1 diabetes, especially if left untreated, make it just as, if not more dangerous. As explained above, type 1 diabetes, unfortunately, shares many symptoms with other conditions and disorders, making it hard to personally diagnose. This is why, upon the onset of anything that could be described as being symptomatic of type 1 diabetes, you should see your doctor immediately just to be safe.