Most cancers are distinguished by where they originate, breast cancer, testicular cancer, and ovarian cancer to name a few. The terms Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma don’t give many clues as to where they originate. To help simplify the disease, you first need to understand what lymphoma means. Lymphoma is cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. This body system carries lymph, a clear fluid, that is a vital part of your immune system.
Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may sound quite similar and do share a few similarities, but they actually have a lot of differences. In this article we analyze the following differences between these conditions…
What is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma, previously known as Hodgkin’s disease, is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is a complex system of lymph nodes, vessels, organs, and tissues that carry lymph, a clear fluid. This system is a vital part of your immune system. “In Hodgkin’s lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally and may spread beyond it,” says the Mayo Clinic.
There are two main types of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, classic and nodular lymphocyte-predominant reports the National Institute for Health. “Classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma is characterized by the presence of both Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells,” says the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Whereas, nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma has lymphocyte-predominant cells, oftentimes called “popcorn cells.”
What is Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a type of cancer that involves the lymphatic system. The cancer starts with lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, that form tumors. Typically, lymphocytes die once they get old and new ones form, but in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, “your lymphocytes don’t die, but continue to grow and divide. This oversupply of lymphocytes crowds into your lymph nodes, causing them to swell,” reports the Mayo Clinic.
There are multiple subtypes of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and your treatment will depend on which type it is. Doctors determine the type by examining many different factors. Finding which lymphocyte is affected, the B cells or the T cells, and how mature the cells were when they become cancerous and other factors will decide which type of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma says the American Cancer Society.
They Both Start in Lymphocytes
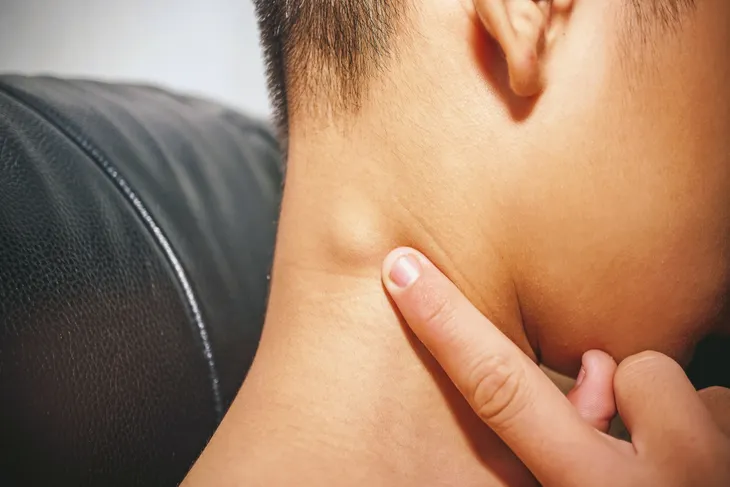
The main similarity between non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Hodgkin’s lymphoma is that both diseases begin in the white blood cell called the lymphocyte, creating swelling within the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are found in the neck, armpit, groin, along the jawline, and in many other spots. They are approximately the size of a pea or bean.
Lymph nodes do slightly enlarge when you are sick from an infection such as a cold or the flu. So, just because you have a large lymph node does not mean you have lymphoma. Oftentimes, doctors will prescribe an antibiotic or check patients for other viral infections before they screen for lymphoma. This is because many other infections produce similar symptoms, including the swollen lymph nodes.
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Symptoms
Hodgkin’s lymphoma causes symptoms that can be attributed to many different conditions. However, it’s important to know what to look for and report them to your doctor if you have them. The symptoms are painless swelling in the lymph nodes of the neck, armpits, or groin, night sweats, weight loss, lack of appetite, tiredness, and itchy skin (especially after a bath or drinking alcohol) says the National Institute of Health.
“Fever for no known reason, weight loss for no known reason, and drenching night sweats are called B symptoms. B symptoms are an important part of staging Hodgkin’s lymphoma and understanding the patient’s chance of recovery,” reports the National Institute of Health. Be sure to keep a record of any symptoms you have and report them to your doctor.
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Symptoms
The symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma will greatly depend on the type of lymphoma and where it is in the body. An example is if the lymphoma started in the lymph nodes in the abdomen you may feel abdominal pain or swelling. If the lymphoma started in the chest or thymus (which produces progenitor cells that mature into T cells) you may have chest pain, difficulty breathing, or coughing.
With all that in mind, the common symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma are as follows: swollen lymph nodes, chills, weight loss, tiredness, easy bruising, chest pain or pressure, and frequent infections says the American Cancer Society. Just as in Hodgkin’s lymphoma, there are B symptoms reports the source. Be sure to let your doctor know if you experience any of these symptoms.
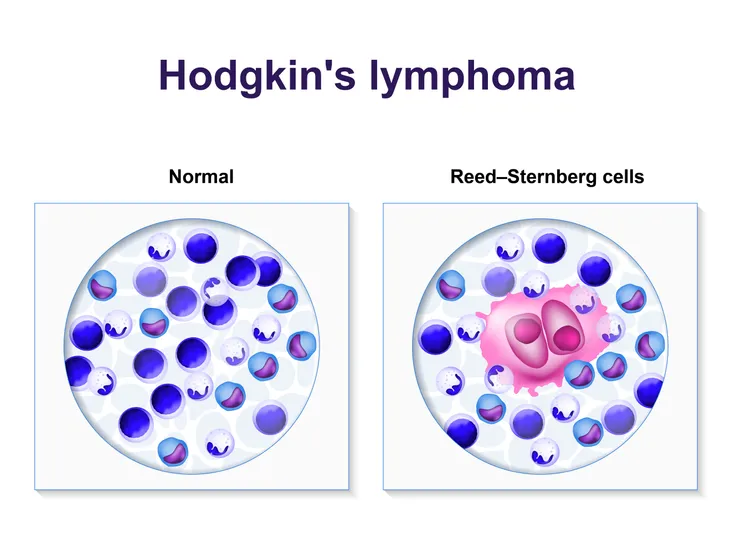
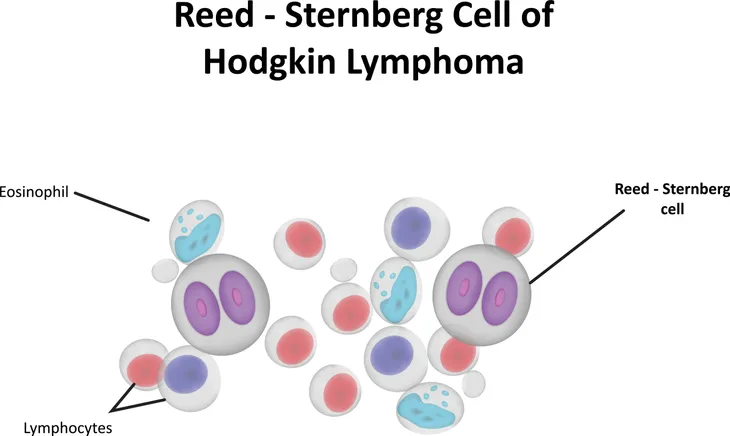
Reed-Sternberg Cells
When looking at the differences between Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma there is one that sticks out as perhaps the most important. Reed-Sternberg cells are mature B cells that have become malignant and are present in Hodgkin’s lymphoma and absent in Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma says the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
A doctor will look at the cancer cells under a microscope. If he or she sees the tell-tale large Reed-Sternberg cells, then it is Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Determining which type of lymphoma will help determine the best course of treatment, the expected progression of the disease, and likely outcomes.
Where It Starts
Another difference between Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is where the disease typically starts in the body. Although both diseases begin within the lymphatic system specifically from where they arise is how they are different. “Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may arise in lymph nodes anywhere in the body, whereas Hodgkin’s lymphoma typically begins in the upper body, such as the neck, chest or armpits” reports the Moffitt Cancer Center.
A doctor will try to determine specifically where the cancer started. This will help them understand where it could or has progressed to and which types of treatments are necessary. While these two diseases are similar, their differences are significant and need to be addressed appropriately.
Risk Factors
There are some risk factors that apply to both Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and there are some risk factors that are unique to only one of the diseases reports the American Cancer Society. The risk factors that apply to both diseases are older age, male gender, family history, and a weakened immune system, such as with HIV or an autoimmune disease.
The source also reports risk factors that are unique to Hodgkin’s lymphoma, such as a previous mononucleosis infection that is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and being in your early 20s. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma specific risk factors are certain chemical and drug exposure, excess weight, breast implants, radiation exposure, Asian or African American descent, and coming from a more developed country.
Diagnosis
People who are diagnosed with lymphoma typically visit their doctor because they have a lump that doesn’t go away or just don’t feel well. The doctor will ask questions about your health history and perform a physical exam, paying extra attention to your lymph nodes, spleen, and liver says the American Cancer Society. Because both Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma have symptoms that overlap with multiple other conditions it can be a difficult diagnosis.
To ultimately diagnose the disease, your doctor will have to perform a biopsy of a lymph node reports the source. This is done by removing an entire lymph node or only a small piece of tissue from the lymph node and having it examined under a microscope by a pathologist to look at the cells.
Prevalence
The American Cancer Society reports the prevalence of Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the United States in 2020 is expected to be 8,480 new diagnoses with 970 deaths. The source reports the average age of diagnosis is 39 years of age. Compared to all cancers, Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a rare cancer.
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is one of the most common cancers in the United States, accounting for about 4-percent of all cancers reports the American Cancer Society. Approximately 77,240 people will be diagnosed with this cancer in 2020, with 19,940 deaths. The source reports that 1 in 41 men and 1 in 52 women will be diagnosed with the disease in their lifetime.
Treatment
Treating lymphoma requires a specialty team of doctors composed of a hematologist, oncologist, radiation oncologist, and sometimes a bone marrow transplant doctor reports the American Cancer Society. Treatment depends on multiple factors including, but not limited to, your overall health, the severity of the disease, and available options.
Treatment for Hodgkin’s lymphoma usually consists of chemotherapy and radiation, says the American Cancer Society. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is also treated with chemotherapy, radiation, other certain medications, and surgery. When someone has a new cancer diagnosis, a team of doctors will work with the patient to develop a treatment plan specific to their circumstances.
Survival Rates
Here’s the good news! Survival rates for people with lymphoma are very high. A survival rate is the percentage of people with a specific type of cancer who live a certain amount of time after their diagnosis. It helps to give you a picture of how successful treatment will be, but it doesn’t say how long you will live.
The 5-year overall survival rate for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is 72-percent. There are multiple types of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma so rates will vary based on the specific type. The 5-year overall survival rate for Hodgkin’s lymphoma is 86-percent. Each patient’s estimated survival rate will vary based on the stage, age, and other health conditions.