- Dementia is a syndrome caused by damage to the brain that can lead to memory loss and a decline in thinking skills.
- Eventually, dementia can result in a mental decline that’s extreme enough to make living independently unfeasible.
- There are three stages of dementia, and each has its own symptoms. Knowing the signs to look for is key to early detection.
- Most forms of dementia are incurable, but there are treatments and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms.
Dementia can be debilitating, making everyday life a challenge. People with dementia can struggle with memory, communication, and even things like walking and personal care. Unfortunately, dementia is an increasingly common syndrome. More than 55 million people live with dementia worldwide, and researchers say that number could triple by 2050.
Given this prediction, recognizing dementia’s symptoms as well as understanding its risk factors is important. Let’s take a closer look at dementia, so you’re aware of the signs, treatments, and lifestyle choices that can help reduce the risk of dementia.
What Is Dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term that refers to a loss of mental abilities and behavioral changes caused by various diseases and injuries. So, dementia itself isn’t a disease. Rather, “it’s a group of symptoms caused by other conditions,” as WebMD puts it.
There are two distinct categories of dementia: cortical dementia and subcortical dementia. According to WebMD, cortical dementia affects the brain’s outer layer, called the cortex, while subcortical dementia affects parts of the brain underneath the cortex. Cortical dementia often causes memory loss and issues with language. Subcortical dementia, on the other hand, commonly leads to slower thinking abilities and difficulty starting activities.
Types and Causes of Dementia
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia, but there are several other types to have on your radar. According to the Mayo Clinic, other common types and causes of dementia include Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Parkinson’s disease, vascular, and Lewy body.
While Alzheimer’s and Creutzfeldt-Jakob diseases are types of cortical dementia, Parkinson’s disease and vascular dementia are types of subcortical dementia. Lewy body dementia affects both parts of the brain, so it’s a cortical and subcortical dementia.
Additionally, there are even more types and causes of dementia, including:
- Huntington’s disease
- Mixed dementia
- Traumatic brain injury
- Frontotemporal dementia
WebMD says dementia can even develop after a stroke, repeated head trauma, and long-time alcohol use. In all of these cases, dementia is caused by damage to the brain.
Symptoms of Dementia
Since dementia is a progressive syndrome, the symptoms change and worsen over time. Common symptoms include memory loss, trouble remembering words, struggling with personal care, and difficulty recognizing loved ones. Symptoms often start relatively mild but become more debilitating as the person moves through the stages of dementia.
The World Health Organization says there are three stages: early-stage dementia, middle-stage dementia, and late-stage dementia. Each stage has its own set of symptoms, which we’ll dig into next. It’s important to keep in mind that dementia affects everyone differently, so these stages should be viewed as a guide instead of an exact sequence.
Early-Stage Dementia
The onset of dementia can be so gradual that many people may not even recognize it in the early stages. People at this stage typically show few signs, but common symptoms include general forgetfulness. For instance, they may misplace belongings, forget common words, or lose track of time. Symptoms may be subtle enough that the person and their loved ones overlook the possibility of dementia.
Impairment is non-existent to mild in the early stages. So, those with early-stage dementia can typically lead independent lives and take care of themselves.
Middle-Stage Dementia
During middle-stage dementia, the symptoms become more apparent. The person may be forgetful of recent events or personal facts. For example, they may have trouble remembering their phone number or people’s names. They may get confused and ask the same question repeatedly. And they may start to wander more or need some help with personal care.
At this stage, the person living with dementia can still take an active role in their life. While they’ll need some assistance, daily activities are still within their capabilities.
Late-Stage Dementia
Once a person reaches late-stage dementia, the symptoms become severe and even more unmistakable. It becomes difficult for the person to communicate, get around, take care of personal health, and recognize loved ones. Around-the-clock help may be needed to get through the day. As a result, this stage is marked by dependency and inactivity.
This stage may even involve noticeable changes in the person’s behavior and personality. For instance, the person may become more aggressive.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re becoming increasingly forgetful, then you’ll want to mention that to your general practitioner. Either bring it up at your annual appointment or pick up the phone now to get their thoughts. And if you notice a loved one is becoming more forgetful, encourage them to see their doctor to talk about the changes.
Depending on the situation and the person’s preferences, they may appreciate you going with them to see the doctor. Then you can help them remember the conversation and offer support.
Diagnosing Dementia
While there isn’t a definitive test to determine whether someone has dementia, doctors can use a combination of methods to make a diagnosis. When you visit your general practitioner, your doctor will likely begin by reviewing your medical history and talking with you about your symptoms. The Mayo Clinic says the doctor may even want to talk about your symptoms with someone who knows you well.
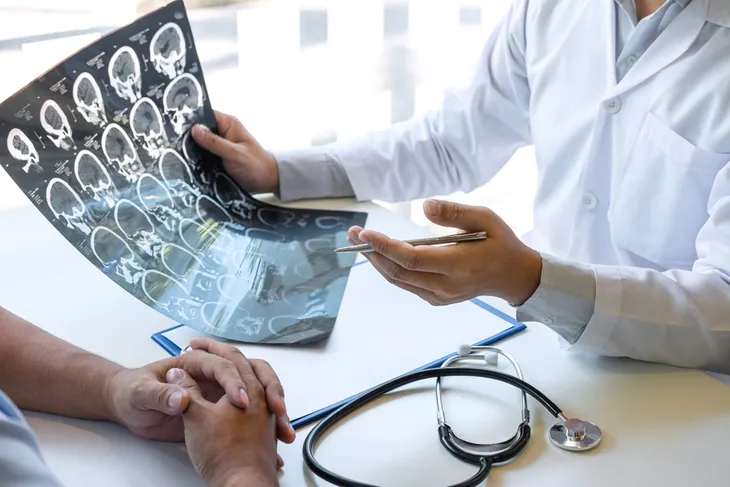
In addition to talking about your medical history and symptoms, the doctor will likely conduct a physical examination. Then your doctor may run more tests or refer you to a specialist. For example, doctors can use cognitive and neurological assessments to evaluate your memory, thinking skills, and language skills. Doctors may want to see brain scans or use laboratory tests to make the diagnosis as well.
Treatments for Dementia
Dementia isn’t curable most of the time. However, the Cleveland Clinic says some medications can help manage symptoms. Although these drugs don’t cure dementia or stop its progression altogether, they may help slow down the stages.
While most types of dementia are incurable and irreversible, the source notes that some dementia disorders can be reversed with treatment. For instance, these forms of dementia include those caused by removable tumors, alcohol use, and head trauma. Ultimately your doctor will determine the best treatment for you.
 novak.elcic / Shutterstock
novak.elcic / ShutterstockLifestyle Changes Can Also Help
Medications and infusions aren’t the only things that can help manage the symptoms of dementia. In fact, the Mayo Clinic recommends a variety of lifestyle and home remedies, including regular exercise, establishing a nighttime routine, and engaging in activities such as gardening, dancing, and painting.
The Mayo Clinic encourages caregivers to make plans for these activities to help the person with dementia focus on things they enjoy and can do. It can also be helpful to keep a calendar with upcoming events, medication schedules, and reminders for daily activities.
Caring for Someone With Dementia
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says more than 16 million Americans take care of family or friends with dementia every year. In 2019, these informal caregivers provided an average of 5-hours of care per day, according to the World Health Organization. Understandably, both the time commitment and emotional toll can be stressful. However, if you stay calm, the Alzheimer’s Association says it’ll help the person you’re caring for.
Other advice for responding to someone with dementia includes showing photos to remind them of loved ones and offering corrections as suggestions. So, instead of sounding scolding, try something like, “Why don’t we go for a walk together?” rather than “You’ll get lost if you go for a walk by yourself.” And even though it can be difficult, try not to take it personally if your loved one forgets family members or family history.
Risk Factors: Age
Several known risk factors contribute to the development of dementia. Some of these risk factors, such as age, can’t be changed. But other factors can be changed to help reduce the risk.
Aging is one of the biggest risk factors. According to the National Institutes of Health, one in seven Americans over the age of 71 have some form of dementia. However, it’s worth noting that the World Health Organization says up to 9-percent of cases are young-onset dementia. That means the person with dementia developed it before the age of 65.
Other Risk Factors
Gender, race, and ethnicity are other risk factors that can’t be changed. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, about two-thirds of Americans with Alzheimer’s are women. Additionally, older Black and Hispanic Americans are more likely to have dementia than white Americans.
While those with a family history of dementia may wonder if they’re at significant risk of inheriting the syndrome, the Alzheimer’s Society says most forms of dementia aren’t passed down to children and grandchildren. In fact, the source notes that more than 99 in 100 cases of Alzheimer’s aren’t inherited.
Dementia Prevention
Although some risk factors of dementia can’t be avoided, others are lifestyle factors that can be modified. Alzheimer’s Disease International says “individuals have a huge potential to reduce their dementia risk.” With this in mind, the source recommends making lifestyle choices that promote good brain and heart health.
For instance, staying fit through diet and exercise as well as avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of dementia. Social isolation is also linked to the development of dementia, so Alzheimer’s Disease International recommends finding ways to stay socially active, like joining a club or community group.