- While all vegetables contain nutrients essential to our well-being, they can be grouped into starchy and non-starchy categories.
- Veggies with less starch typically have fewer calories and carbohydrates and more fiber.
- Our bodies absorb low-starch vegetables more slowly than starchy vegetables, helping to control blood sugar.
- Non-starchy vegetables are also associated with weight loss.
- Mushrooms, brussels sprouts, green beans, cauliflower, and leafy greens are examples of non-starchy vegetables.
The next time you’re in the produce aisle, consider filling your basket with a variety of non-starchy vegetables. All veggies offer nutritional rewards, but ones low in starch typically have fewer carbohydrates and calories, and more water and fiber.
Explore the benefits of non-starchy vegetables below. We’ll highlight ones that deserve a spot on your plate and provide ideas on how to prepare them to add variety and interest to your meals.
Benefits of Non-Starchy Vegetables
Starches are a type of carbohydrate that the body breaks into glucose for energy. Vegetables that are light on starch have fewer carbohydrates and calories.
Starchy vegetables, such as potatoes, yams, corn, and peas, contain about 15-grams of carbohydrates per serving. Non-starchy vegetables, including brussels sprouts, radishes, asparagus, and broccoli, contain about 5-grams of carbohydrates per serving.
Non-starchy veggies fit well into low-carb, Paleo, keto, and diabetic diets and offer several benefits compared to starchy ones:
- They contain more water and fiber to help keep you full.
- They’re absorbed more slowly and don’t cause as rapid a rise in blood sugar.
- They have fewer calories and may help with weight loss, according to researchers at Harvard’s School of Public Health.
Adding Non-Starchy Vegetables to Your Diet
The World Health Organization (WHO) provides further guidance, distinguishing between the types of vegetables you should be eating. The WHO recommends five portions of fruit and vegetables per day, but starchy root vegetables, such as potatoes and sweet potatoes, don’t count toward those portions.
An easy way to achieve a diet rich in non-starchy vegetables is to follow the Diabetes Plate Method, even if you don’t have diabetes. This approach to healthy eating involves filling half of your plate with non-starchy veggies, one quarter with proteins, and one quarter with carbohydrates. Aim for a variety of vegetables and colors.
Read on for ideas of nutritious, non-starchy vegetables to load onto your plate.
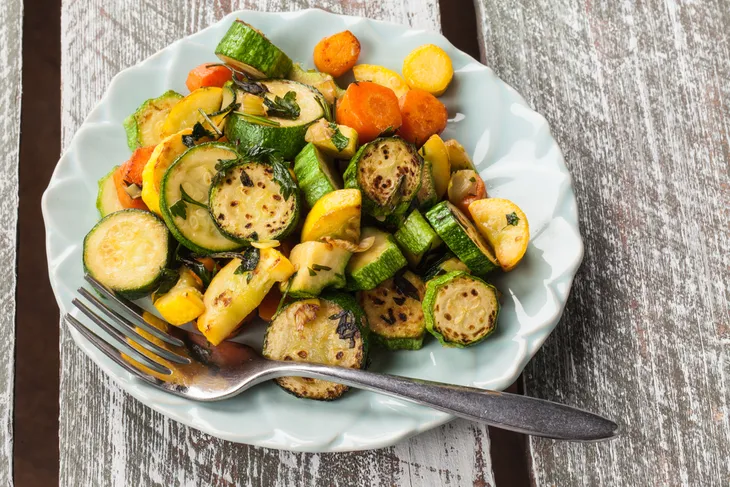
Summer Squash
While acorn, butternut, and other winter squashes are starchy, their summer cousins fall into the non-starchy category. Summer squash includes yellow squash (both straight neck and crookneck varieties), zucchini (yellow and green), cousa, chayote, and patty pan. These foods are a good source of vitamins A, C, and B6, as well as potassium and manganese.
Unlike winter squash, summer squash has a soft exterior and doesn’t need peeling. You can eat the skin, flesh, and seeds. Try a summer vegetable tian, and roast a variety of squash with tomatoes, onions, olive oil, and garlic. For a low-carb alternative to pasta, spiralize zucchini and turn it into noodles.
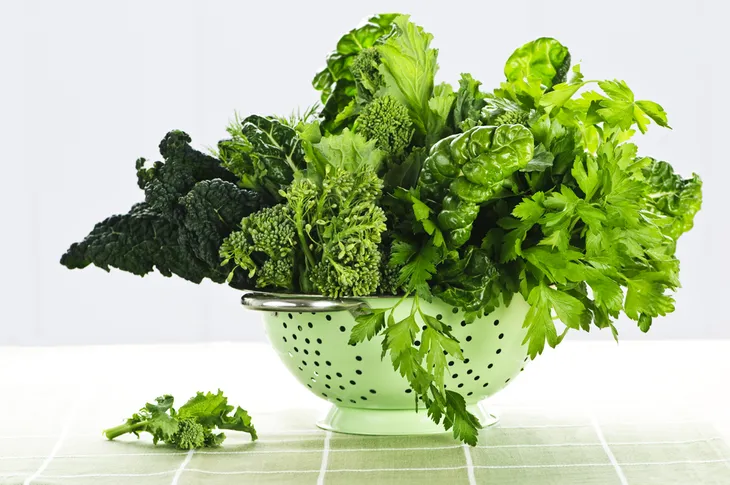
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are a bounty of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folic acid and potassium. While all fruits and veggies are good for your health, green leafy vegetables are most strongly associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease, according to research from the Harvard School of Public Health.
Leafy greens include kale, mustard greens, chard, spinach, dandelion, watercress, and endive, giving you plenty of ways to bolster your diet. Sauté or steam collard greens as a side dish, or layer arugula into a sandwich. You can blend spinach into smoothies and bake kale leaves into chips.
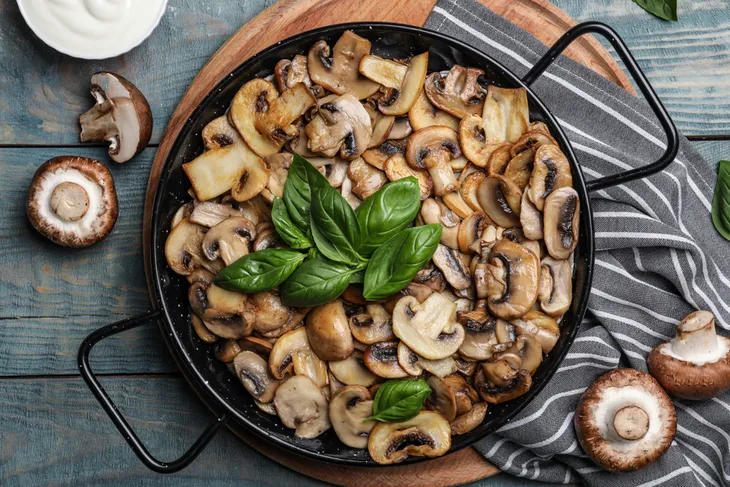
Mushrooms
Although mushrooms are a fungus, the U.S. Department of Agriculture considers them a vegetable for nutritional purposes. This superfood is loaded with 15 vitamins and minerals, including B2, B3, folate, B5, selenium, copper, and phosphorus. They’re low in sodium, saturated fat, and cholesterol.
Mushrooms are savory and satisfying, whether you opt for white button, cremini, oyster, portobello, or shiitake mushrooms. Many consumers are turning to this food to reduce meat intake. You can marinate and grill a portobello mushroom and serve it like a burger, or replace up to half of ground meat with chopped mushrooms in a recipe to transition to eating fewer animal proteins. Mushrooms can also be tossed into stir-fry, soups, and salads and sprinkled on top of pizza.
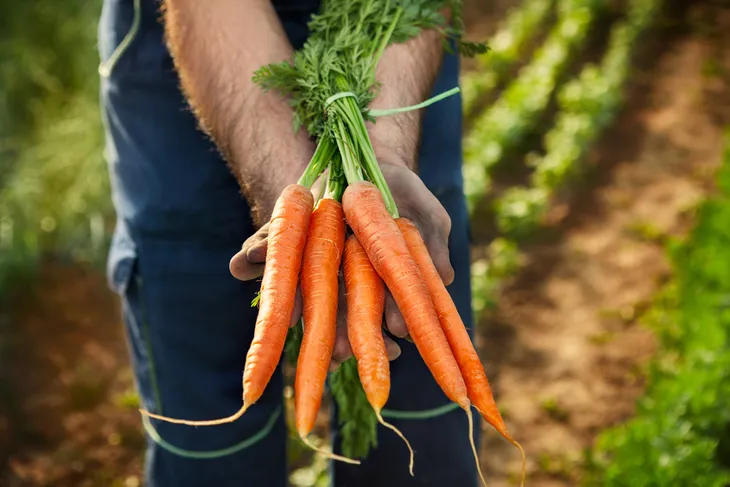
Carrots
Carrots are rich in beta-carotene, an antioxidant that the body turns into vitamin A. In fact, you’re about three-quarters of the way to your recommended daily amount of vitamin A with a half-cup of carrots. This root vegetable also delivers vitamins K, C, and potassium. Orange carrots contain the most beta-carotene, which is needed to support strong immune systems and eye health. Yellow and purple carrots also have benefits.
Carrots are easy to add to your diet because they can be consumed raw, and kids often enjoy the sweetness and crunch. Carrots can also be roasted, steamed, and added to soups and stews.
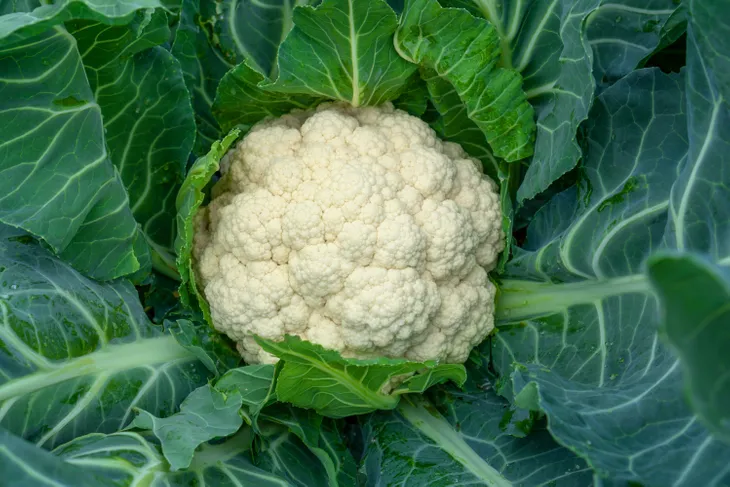
Cauliflower
Some people find it hard to get excited about cauliflower, but this cruciferous vegetable is bursting with vitamin C, potassium, folate, and calcium. You can now find different color varieties alongside white cauliflower at the grocery store, adding visual interest to your plate. Colored cauliflower also serves up extra health benefits. Orange cauliflower contains carotenoids, and purple cauliflower boasts anthocyanin – both important antioxidants!
If you don’t want to spend time chopping a cauliflower head into florets, roast it whole. You can serve mashed cauliflower instead of potatoes for a low-carb side dish, or run cauliflower through the food processor and make a pizza crust. Look in the freezer aisle of your supermarket for convenient frozen cauliflower rice.
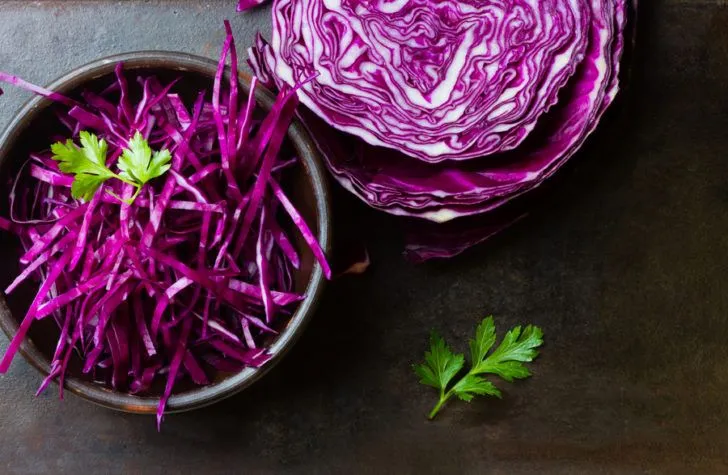
Cabbage
Make room on your dinner plate for nutrient-dense cabbage, which is rich in potassium, folate, and vitamins C and K. This veggie may help reduce inflammation, promote better digestion, and lower blood pressure and cholesterol, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
You can choose from a few types of cabbage. Green and red cabbage often take center stage in coleslaw, salads, kimchi, sauerkraut, cabbage rolls, and dishes such as corned beef and cabbage. Bok choy and Chinese cabbage — also known as Napa cabbage — brighten stir-fries and Asian-inspired dishes. Sautéed savoy cabbage, with its delicately crinkled leaves, makes an elegant but simple side dish.
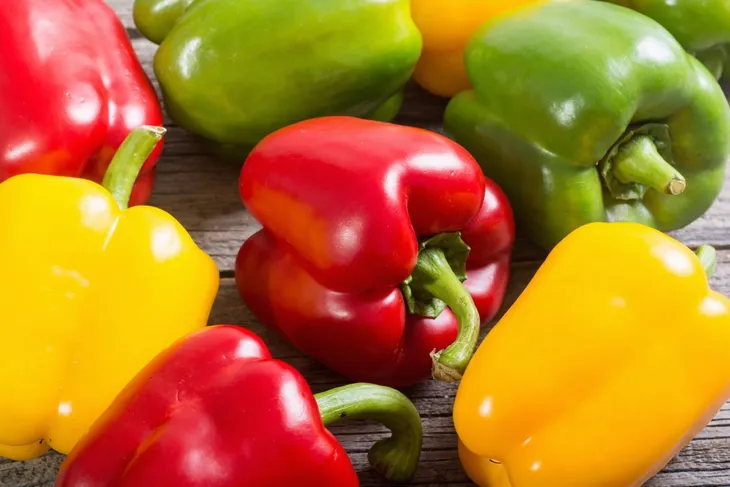
Bell Peppers
It’s simple to add a rainbow of color to your diet with sweet bell peppers. Whether you choose green, orange, yellow, or red peppers, you’ll get a good helping of potassium, folic acid, and vitamins A and C. The nutritional profile varies slightly between the different colored peppers, but any bell pepper is an excellent source of nutrients. Snack on peppers raw, or enjoy them roasted, stir-fried, and stuffed.
Green peppers have more polyphenols, a powerful antioxidant compound. According to Tufts University Health & Nutrition Letter, red peppers, which get their ruby hue from beta-carotene, typically have the most carotenoids. Orange peppers are rich in lutein, which supports cognitive function and healthy vision. Yellow peppers have twice the vitamin C of green peppers.
 AlexeiLogvinovich / Shutterstock
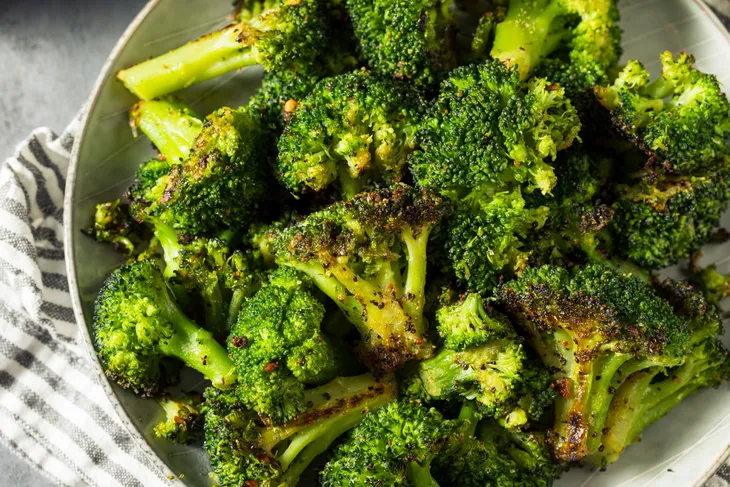
AlexeiLogvinovich / ShutterstockBroccoli and Broccolini
Broccoli has always been a mainstay on dinner plates, whether it’s steamed, roasted, or starring in a broccoli salad. For a fresh twist on this classic vegetable, consider broccolini. This member of the cabbage family is a hybrid of broccoli and Chinese broccoli (gai lan), with a thinner stalk and smaller florets than broccoli.
You can grill, sauté and steam this mild-tasting vegetable, and you don’t need to peel the stem. It’s more tender than broccoli and faster to cook. Broccolini adds vitamins A and C to your diet, as well as calcium, iron, and potassium.
 Shutterstock/Brent Hofacker
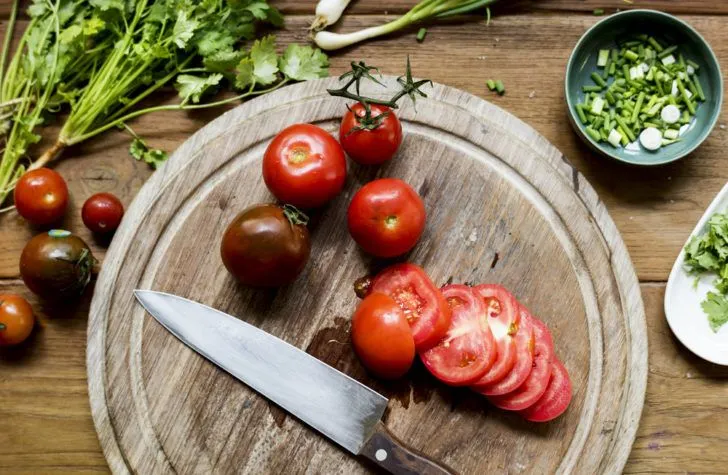
Shutterstock/Brent HofackerTomatoes
In addition to packing plenty of vitamin C, potassium, and vitamin K, tomatoes are an excellent source of lycopene. Studies suggest this antioxidant may help reduce damage by free radicals, as well as potentially lower the risk of different cancers. Lycopene lends a red hue to foods, so the brighter the tomato, the more lycopene it usually contains.
You can enjoy the health benefits of tomatoes in many ways, whether you reach for cherry, beefsteak, or Roma tomatoes. Many of us already add tomatoes to sandwiches and salads. You can also make fresh salsa, stuffed tomatoes, and tasty, sandwich-style tomato stacks.
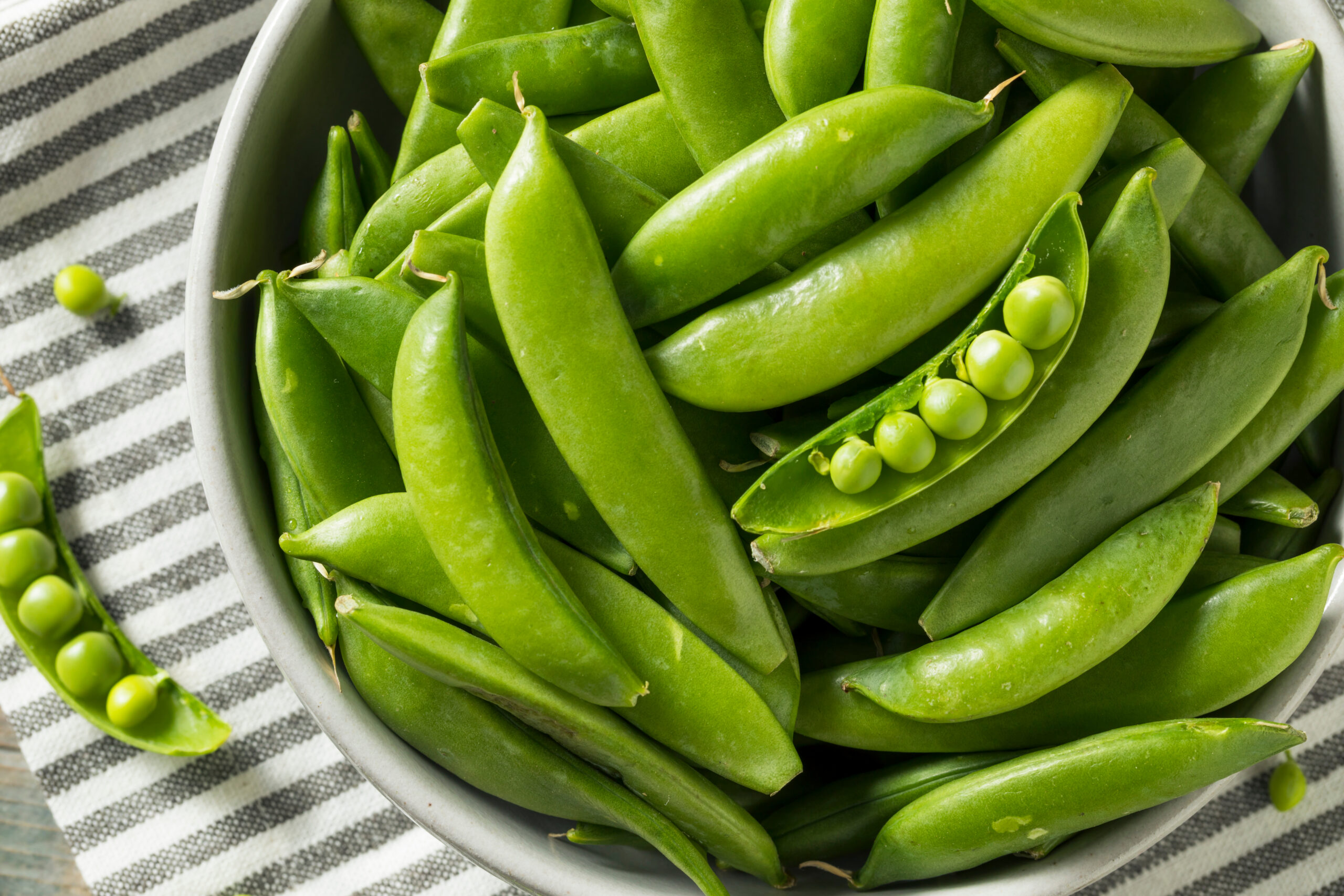
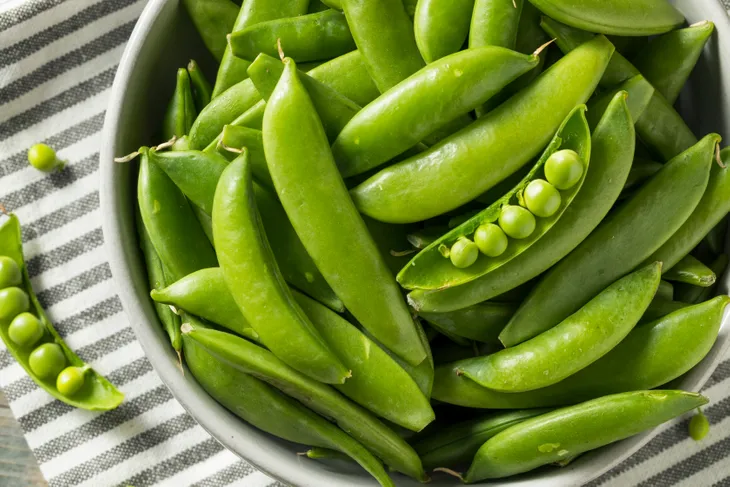
Sugar Snap Peas
Sugar snap peas are sweet, crisp, and flavorful, and they have an edible shell. They can be consumed fresh or added to stir-fries for a pleasant, crunchy texture. Snap peas are chock-full of vitamins A, C, and K, helping to boost immunity and bone health.
Snow peas, which are flatter than snap peas, have a similar nutritional profile and are also non-starchy. It gets confusing when garden peas enter the picture, though. These green peas are considered starchy vegetables, containing about 15 grams of carbohydrates per half-cup. Green peas must be shelled before eating and are often found frozen or canned at the supermarket.