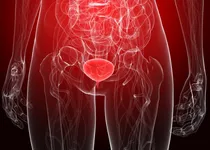
 A urinary tract infection involves the bacterial infection of the bladder which can move into the kidneys if left untreated. The condition is more common in women than men, with sexual activity being one of the major causes of infection in young women. Symptoms of a urinary tract infection include frequent and urgent urination, a burning sensation during urination, and pain in the lower back or kidney area. Pus or blood may also be present in the urine. Most urinary tract infections can be managed relatively easily with oral antibiotics, though intravenous antibiotics may be required in more serious cases.
A urinary tract infection involves the bacterial infection of the bladder which can move into the kidneys if left untreated. The condition is more common in women than men, with sexual activity being one of the major causes of infection in young women. Symptoms of a urinary tract infection include frequent and urgent urination, a burning sensation during urination, and pain in the lower back or kidney area. Pus or blood may also be present in the urine. Most urinary tract infections can be managed relatively easily with oral antibiotics, though intravenous antibiotics may be required in more serious cases.

