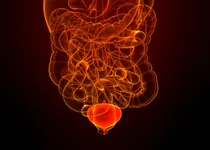
 Patients with an overactive bladder experienced increased frequency and urgency of urination, and may also experience urinary incontinence. Typically, doctors diagnose overactive bladder if the aforementioned symptoms are present and the patient urinates in excess of eight times per day. Age is the primary risk factor of overactive bladder; most patients with the condition are over the age of 50. Treatment may include limiting fluid intake, reducing or limiting caffeine consumption, and avoiding diuretics such as alcohol. Drugs which reduce the need to urinate frequently and alleviate the sense of urinary urgency may also be given, and are particularly effective in patients who experience symptoms nocturnally.
Patients with an overactive bladder experienced increased frequency and urgency of urination, and may also experience urinary incontinence. Typically, doctors diagnose overactive bladder if the aforementioned symptoms are present and the patient urinates in excess of eight times per day. Age is the primary risk factor of overactive bladder; most patients with the condition are over the age of 50. Treatment may include limiting fluid intake, reducing or limiting caffeine consumption, and avoiding diuretics such as alcohol. Drugs which reduce the need to urinate frequently and alleviate the sense of urinary urgency may also be given, and are particularly effective in patients who experience symptoms nocturnally.

