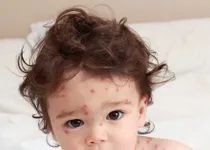
 Infection with the varicella zoster virus leads to chicken pox, a contagious disease initially marked by headaches, muscle aches, nausea, malaise and loss of appetite. As the disease continues to run its course, skin lesions and a fever develop. Chicken pox is highly contagious, though people who have had it once become immune to future occurrences. While the disease is largely associated with childhood, it can also affect adults and is in fact a far more dangerous condition in adults. Antiviral medications are usually used to treat chicken pox, but because it is a viral disease, there is no cure. Palliative measures may also be taken to reduce the swelling and itchiness of skin lesions.
Infection with the varicella zoster virus leads to chicken pox, a contagious disease initially marked by headaches, muscle aches, nausea, malaise and loss of appetite. As the disease continues to run its course, skin lesions and a fever develop. Chicken pox is highly contagious, though people who have had it once become immune to future occurrences. While the disease is largely associated with childhood, it can also affect adults and is in fact a far more dangerous condition in adults. Antiviral medications are usually used to treat chicken pox, but because it is a viral disease, there is no cure. Palliative measures may also be taken to reduce the swelling and itchiness of skin lesions.

